来自A level and IG Revision Wiki
跳到导航
跳到搜索
|
|
| 第133行: |
第133行: |
|
| |
|
| ==Essay - Micro微观== | | ==Essay - Micro微观== |
| | | {| |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''题目2'''|| || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File:9708-2023-specimen-paper-4_2.png|800px]] |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" |'''题目类型'''|| || '''政策评价''' |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''难度''' || || {{Background color|red|{{color|white|''' 困难 '''}}}} |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''考察知识点'''|| || market failure;externality的概念、原因及影响;政府纠正positive externality的各类政策 |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点'''|| || ● 首先解释market failure的概念,提到externality是其原因之一。<br/>● 再解释externality的概念,着重介绍positive externality的概念、公式、例子、分类(生产和消费两种类型),以及带来的影响(问题),此处需要画图解释。<br/>● 接着讨论政府可用的政策,讨论2~3个政策比较保险。每种政策需要指明实施的具体政策手段(1句话概述),成功实施会纠正外部性的逻辑链,以及该政策可能带来的问题(负面影响)。如果能够画图,则需要带图说明。<br/>● 最后对上文观点进行总结并回答题干问题,政府干预可能会纠正,但也存在新的问题需要解决。 |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''官方答案'''|| || style="background: #d3d3d3"| [[File:9708-2023-specimen-paper-4_2-MS.png|600px]] |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''文字版备查'''|| ||<small>2 With the help of a diagram, assess the view that government intervention can be used successfully to correct market failure caused by positive externalities. [20]</small> |
| | |} |
| | <br/> |
| | {| |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''题目3'''|| || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File:9708-2023-specimen-paper-4_3.png|800px]] |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" |'''题目类型'''|| || '''观点讨论''' |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''难度''' || || {{Background color|red|{{color|white|''' 困难 '''}}}} |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''考察知识点'''|| || 非竞争的劳动力市场 |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点'''|| || ● 首先解释perfect competition的劳动力市场特征,进而引出imperfect competition的劳动力市场特征。<br/>● 然后先肯定题中观点,确实有可能存在低工资高失业的情况,即monopsony的时候。画出图像并解释其就业情况,指出后果。<br/>● 接着说明如果碰到低工资高失业的情况,政府应如何解决,谈论一些解决办法及可能新带来的负面影响。<br/>● 然后指出还有其他情况,即trade union、bilateral monopoly的情况,分别画图进行解释,分析其工资和失业情况,与之前做对比。<br/>● 最后进行总结与回答题干问题,并非always。 |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''官方答案'''|| || style="background: #d3d3d3"| [[File:9708-2023-specimen-paper-4_3-MS.png|600px]] |
| | |- |
| | | align="right" valign="top" |'''文字版备查'''|| ||<small>3 With the help of a diagram, assess whether imperfect labour markets will always lead to lower wages and higher unemployment. [20]</small> |
| | |} |
| | <br/> |
|
| |
|
| ==Essay - Macro宏观== | | ==Essay - Macro宏观== |
2022年8月15日 (一) 02:33的版本
整卷下载
关于难度分类的说明:
容易 :概念类、识别类、公式计算类
中等 :原因分析类、影响分析类、图像分析类、计算分析类
困难 :全新概念类、全新场景类、全新图像类、推导复杂类、观点评价类、对比评价类、政策评价类
Data response

中英对照
| 原文 |
参考译文(谷歌机翻)
|
Loyalty and consumer behaviour
Consumer loyalty can be shown in different ways. It may be through:
• customer reward schemes (e.g. loyalty cards) that offer discounts based on the amount spent with a specific retailer
• emotional loyalty where customers prefer a particular brand that they always buy
• monopoly loyalty where there is no alternative to the retailer or brand.
Supermarkets try to attract customers by using loyalty cards that give promotions and price reductions to those who have a card. The cards also help the supermarket build barriers between retailers to gain a marketing advantage.
When consumers are collecting points towards a particular goal, the loyalty card may hinder free competition and prevent switching between brands. However, sometimes the discounts used by the scheme may be confusing and make it difficult for the consumer to compare prices.
There are risks for the retailers too. The loyalty cards require substantial investment to run – one supermarket put the cost at US$60m a year. These costs could well result in higher prices for the consumer.
But how do loyalty card schemes fit into the context of the way in which consumers make choices? A research report found that in one country where 70% of consumers had a loyalty card, only about 10% were loyal to one particular card.
It has been found that when choosing to buy groceries consumers look for one-stop shopping (43%), good service (22%), price (18%), the availability of a coffee shop (12%) and help with packing (6%). Loyalty cards come below these.
Companies use loyalty cards to gather data on customers and their buying preferences. They then direct future offers to consumer wishes in specific promotions both online and in the mail. Loyalty schemes are thus sometimes less about loyalty and more about understanding customers’ wants.
The economic model of consumer behaviour using indifference curves assumes that consumers conduct research and buy products and services in a rational way. Many purchases, however, are based on habit and consumer research is imprecise. When the consumer has a low involvement in research or a low emotional attachment to the product, there will be little loyalty.
|
忠诚度和消费者行为
消费者忠诚度可以通过不同的方式表现出来。可能是通过:
• 客户奖励计划(例如会员卡),根据在特定零售商处的消费金额提供折扣
• 情感忠诚度,客户更喜欢他们经常购买的特定品牌
• 零售商或品牌别无选择的垄断忠诚度。
超市试图通过使用会员卡来吸引顾客,这些会员卡为持有卡的人提供促销和降价服务。这些卡片还帮助超市在零售商之间建立障碍,以获得营销优势。
当消费者为特定目标收集积分时,会员卡可能会阻碍自由竞争并阻止品牌之间的转换。但是,有时该计划使用的折扣可能会令人困惑,使消费者难以比较价格。
零售商也存在风险。会员卡需要大量投资才能运行——一家超市将成本定为每年 6000 万美元。这些成本很可能导致消费者价格上涨。
但是,会员卡计划如何适应消费者做出选择的方式呢?一份研究报告发现,在一个 70% 的消费者拥有会员卡的国家/地区,只有大约 10% 的人对一张特定的卡有忠诚度。
研究发现,消费者在选择购买杂货时会考虑一站式购物(43%)、优质服务(22%)、价格(18%)、咖啡店的可用性(12%)和包装帮助( 6%)。忠诚卡低于这些。
公司使用会员卡来收集有关客户及其购买偏好的数据。然后,他们通过在线和邮件的特定促销活动将未来的报价直接满足消费者的愿望。因此,忠诚度计划有时不是关于忠诚度,而是更多地了解客户的需求。
使用无差异曲线的消费者行为经济模型假设消费者以理性的方式进行研究并购买产品和服务。然而,许多购买都是基于习惯,而消费者研究并不精确。当消费者对研究的参与度低或对产品的情感依恋度低时,忠诚度就会很低。
|
| 题目1a |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
imperfect competition的特征
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 从文中摘录能够说明市场中存在门槛、存在imperfect knowledge等满足不完全竞争市场特征的句子,来证明loyal cards使得市场不完全竞争。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(a) What evidence is there in the article to suggest that loyalty cards make markets imperfectly competitive? [4]
|
| 题目1b |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
PED与TR的关系;企业的目标
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● loyalty使得PED偏向inelastic,因此企业可以通过涨价增加TR,在成本不变时提升profit,尽量实现利润最大化。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(b) Explain why a profit-maximising retailer may be interested in the link between consumers’ loyalty and price elasticity of demand. [4]
|
| 题目1c |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
观点讨论
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
价格歧视
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 先从能提供价格折扣的loyalty cards确实对企业很有帮助来讨论。比如能够招揽客户、发现客户的偏好等。
● 再从能提供价格折扣的loyalty cards并没有太多帮助来讨论。比如价格并非人们最看重的因素、人们可能根据自己的习惯、离家远近、装潢等原因选择。
● 最后做出回答,表示确实存在一些conflicting evidence。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(c) Consider whether there is conflicting evidence in the article about the effectiveness of loyalty cards which offer price discounts. [5]
|
| 题目1d |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析(含画图)
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
rational behaviour;indifference curve
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 先对rational behaviour进行解释,说明消费者需要utility最大化。
● 接着介绍indifference curve与budget line的相关概念,画出二者相切的图像,说明该处是理性消费者的最佳选择。
● 然后结合该理论的局限性说明如何实现理论中的理性,比如需要对两种商品无喜好偏向、有perfect information、能够计算出utility的数值、不存在uncertainty的情况等。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(d) Assess how the idea of rationality is used in the indifference curve theory of consumer behaviour. [7]
|
Essay - Micro微观
| 题目2 |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
政策评价
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
market failure;externality的概念、原因及影响;政府纠正positive externality的各类政策
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 首先解释market failure的概念,提到externality是其原因之一。
● 再解释externality的概念,着重介绍positive externality的概念、公式、例子、分类(生产和消费两种类型),以及带来的影响(问题),此处需要画图解释。
● 接着讨论政府可用的政策,讨论2~3个政策比较保险。每种政策需要指明实施的具体政策手段(1句话概述),成功实施会纠正外部性的逻辑链,以及该政策可能带来的问题(负面影响)。如果能够画图,则需要带图说明。
● 最后对上文观点进行总结并回答题干问题,政府干预可能会纠正,但也存在新的问题需要解决。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
2 With the help of a diagram, assess the view that government intervention can be used successfully to correct market failure caused by positive externalities. [20]
|
| 题目3 |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
观点讨论
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
非竞争的劳动力市场
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 首先解释perfect competition的劳动力市场特征,进而引出imperfect competition的劳动力市场特征。
● 然后先肯定题中观点,确实有可能存在低工资高失业的情况,即monopsony的时候。画出图像并解释其就业情况,指出后果。
● 接着说明如果碰到低工资高失业的情况,政府应如何解决,谈论一些解决办法及可能新带来的负面影响。
● 然后指出还有其他情况,即trade union、bilateral monopoly的情况,分别画图进行解释,分析其工资和失业情况,与之前做对比。
● 最后进行总结与回答题干问题,并非always。
|
| 官方答案 |
|
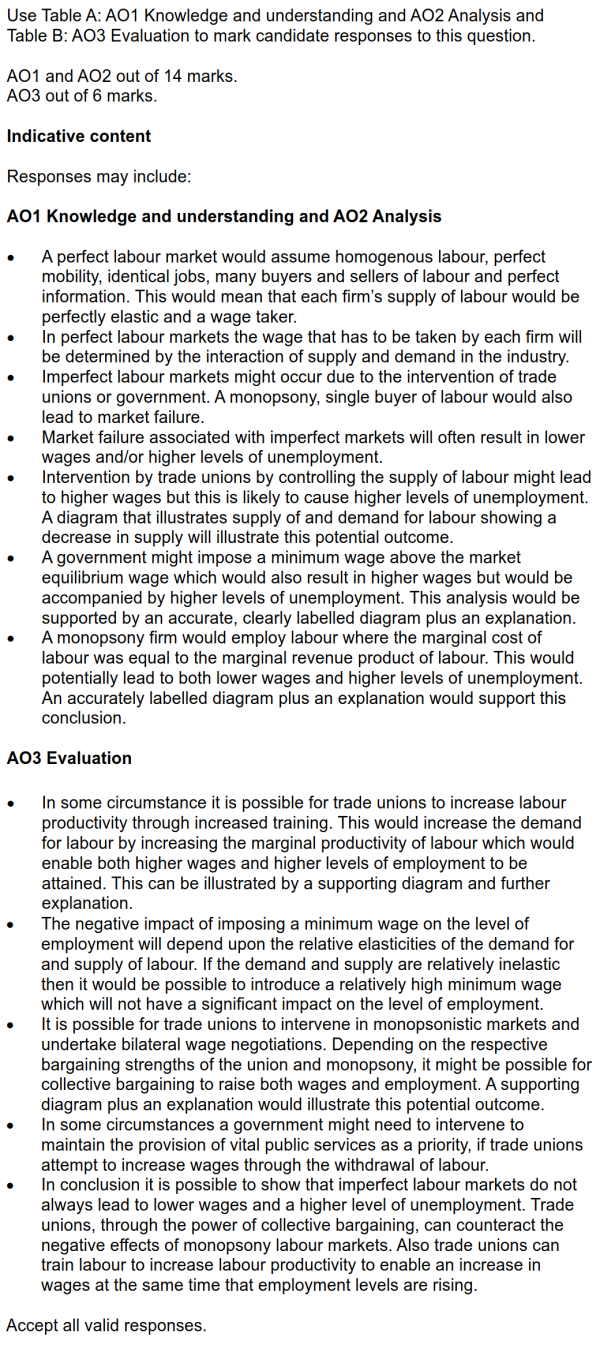
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
3 With the help of a diagram, assess whether imperfect labour markets will always lead to lower wages and higher unemployment. [20]
|
Essay - Macro宏观












