“Edexcel IG revision - 2.2 (2019)”的版本间的差异
| (未显示同一用户的5个中间版本) | |||
| 第7行: | 第7行: | ||
=2.2 The global economy 全球经济= | =2.2 The global economy 全球经济= | ||
==2.2.1 Globalisation 全球化== | ==2.2.1 Globalisation 全球化== | ||
*{{color|red| | *{{color|red|'''大纲要求'''}} | ||
[[File:EdexcelIG2019-2.2.1要求.png|800px]] | [[File:EdexcelIG2019-2.2.1要求.png|800px]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| 第21行: | 第21行: | ||
***There is a free exchange of technology and intellectual property across borders. 技术和知识产权可以在国际间自由往来。 | ***There is a free exchange of technology and intellectual property across borders. 技术和知识产权可以在国际间自由往来。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===b) Reasons for globalisation: 全球化的原因=== | ===b) Reasons for globalisation: 全球化的原因=== | ||
• fewer tariffs and quotas | {{color|grey| | ||
• reduced cost of transport | • fewer tariffs and quotas<br/> | ||
• reduced cost of communication | • reduced cost of transport<br/> | ||
• increased significance of multinational corporations (MNCs). | • reduced cost of communication<br/> | ||
• increased significance of multinational corporations (MNCs).<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*全球化的原因: | *全球化的原因: | ||
| 第33行: | 第35行: | ||
**increased significance of multinational corporations (MNCs) 跨国公司的重要性:跨国公司数量的上升,有助于各国之间的商品和服务的流动,促进各国之间的联系。 | **increased significance of multinational corporations (MNCs) 跨国公司的重要性:跨国公司数量的上升,有助于各国之间的商品和服务的流动,促进各国之间的联系。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===c) Impacts of globalisation and global companies on individual countries, governments, producers and consumers, workers and the environment: 全球化的影响及国际企业对单个国家、政府、生产者与消费者、工人和环境的影响=== | ===c) Impacts of globalisation and global companies on individual countries, governments, producers and consumers, workers and the environment: 全球化的影响及国际企业对单个国家、政府、生产者与消费者、工人和环境的影响=== | ||
• rising living standards | {{color|grey| | ||
• greater choice | • rising living standards<br/> | ||
• lower prices | • greater choice<br/> | ||
• reduced costs of communication | • lower prices<br/> | ||
• closing of traditional industries | • reduced costs of communication<br/> | ||
• environmental impact. | • closing of traditional industries<br/> | ||
• environmental impact.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*全球化的影响: | *全球化的影响: | ||
| 第54行: | 第58行: | ||
**environmental impact全球化对环境有一定影响。技术的进步和交流可能会改善环境,但大量交通工具的使用、生产扩张也会导致大量污染物排放,污染环境。跨国公司可能会大量消耗当地的资源,导致资源枯竭。 | **environmental impact全球化对环境有一定影响。技术的进步和交流可能会改善环境,但大量交通工具的使用、生产扩张也会导致大量污染物排放,污染环境。跨国公司可能会大量消耗当地的资源,导致资源枯竭。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===d) Definition of multinational corporations (MNCs): 跨国公司的定义=== | ===d) Definition of multinational corporations (MNCs): 跨国公司的定义=== | ||
• definition of foreign direct investment (FDI) | {{color|grey| | ||
• reasons for emergence of MNCs/FDI: | • definition of foreign direct investment (FDI)<br/> | ||
• reasons for emergence of MNCs/FDI:<br/> | |||
o to benefit from economies of scale<br/> | |||
o to access natural resources/cheap materials<br/> | |||
o lower transport and communication costs<br/> | |||
• advantages and disadvantages of MNCs/ FDI: | o to access customers in different regions.<br/> | ||
• advantages and disadvantages of MNCs/ FDI:<br/> | |||
o creating jobs<br/> | |||
o investing in infrastructure<br/> | |||
o developing skills<br/> | |||
o developing capital<br/> | |||
o contributing to taxes<br/> | |||
o avoiding paying taxes<br/> | |||
o environmental damage<br/> | |||
o moving profits abroad.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*Foreign direct investment(FDI):外国直接投资。指的是在外国建厂生产或购买外国当地企业,这会给当地带来capital flows资金流。 | *Foreign direct investment(FDI):外国直接投资。指的是在外国建厂生产或购买外国当地企业,这会给当地带来capital flows资金流。 | ||
| 第99行: | 第105行: | ||
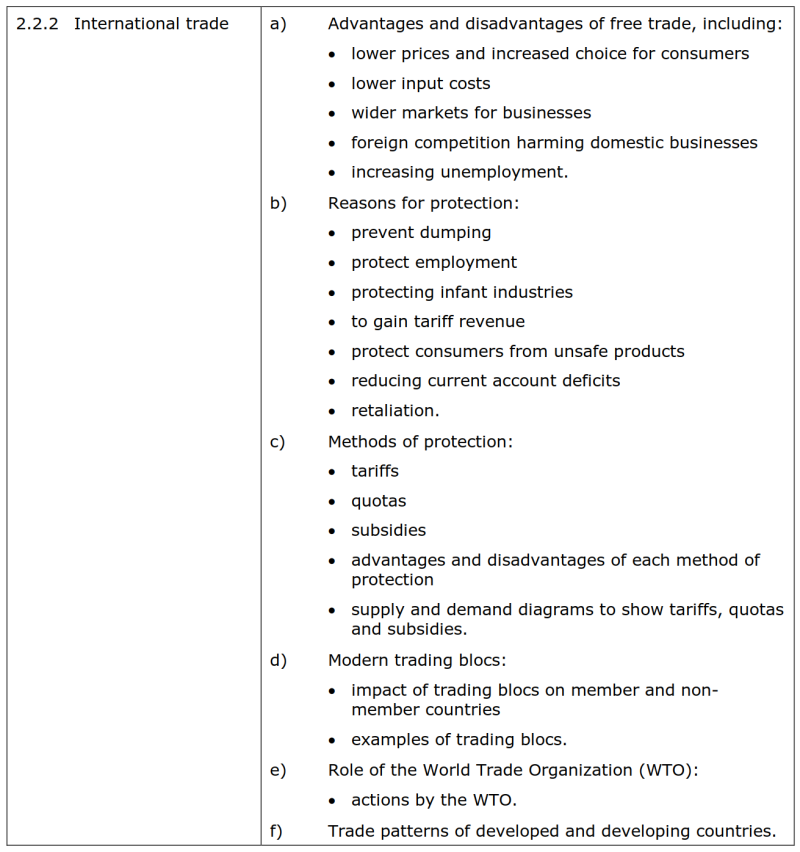
==2.2.2 International trade 国际贸易== | ==2.2.2 International trade 国际贸易== | ||
*{{color|red| | *{{color|red|'''大纲要求'''}} | ||
[[File:EdexcelIG2019-2.2.2要求.png|800px]] | [[File:EdexcelIG2019-2.2.2要求.png|800px]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| 第105行: | 第111行: | ||
===a) Advantages and disadvantages of free trade, including: 自由贸易的优缺点=== | ===a) Advantages and disadvantages of free trade, including: 自由贸易的优缺点=== | ||
• lower prices and increased choice for consumers | {{color|grey| | ||
• lower input costs | • lower prices and increased choice for consumers<br/> | ||
• wider markets for businesses | • lower input costs<br/> | ||
• foreign competition harming domestic businesses | • wider markets for businesses<br/> | ||
• increasing unemployment. | • foreign competition harming domestic businesses<br/> | ||
• increasing unemployment.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*Free trade:自由贸易,即没有贸易壁垒,市场可以自由决定进出口的数量和种类。 | *Free trade:自由贸易,即没有贸易壁垒,市场可以自由决定进出口的数量和种类。 | ||
| 第124行: | 第131行: | ||
**Vulnerability经济更加脆弱,依赖性强,容易受到外界冲击。 | **Vulnerability经济更加脆弱,依赖性强,容易受到外界冲击。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===b) Reasons for protection: 贸易保护的原因=== | ===b) Reasons for protection: 贸易保护的原因=== | ||
• prevent dumping | {{color|grey| | ||
• protect employment | • prevent dumping<br/> | ||
• protecting infant industries | • protect employment<br/> | ||
• to gain tariff revenue | • protecting infant industries<br/> | ||
• protect consumers from unsafe products | • to gain tariff revenue<br/> | ||
• reducing current account deficits | • protect consumers from unsafe products<br/> | ||
• retaliation | • reducing current account deficits<br/> | ||
• retaliation<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*Protectionism:贸易保护主义。通过一系列政策强制干预正常贸易,设置trade barriers贸易门槛,达到减少进口或增加出口的目的。 | *Protectionism:贸易保护主义。通过一系列政策强制干预正常贸易,设置trade barriers贸易门槛,达到减少进口或增加出口的目的。 | ||
| 第155行: | 第164行: | ||
***如果外国对本国实施了贸易保护,本国也可以对外国实施贸易保护以反制。 | ***如果外国对本国实施了贸易保护,本国也可以对外国实施贸易保护以反制。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===c) Methods of protection: 贸易保护的方式=== | ===c) Methods of protection: 贸易保护的方式=== | ||
• tariffs | {{color|grey| | ||
• quotas | • tariffs<br/> | ||
• subsidies | • quotas<br/> | ||
• advantages and disadvantages of each method of protection | • subsidies<br/> | ||
• supply and demand diagrams to show tariffs, quotas and subsidies. | • advantages and disadvantages of each method of protection<br/> | ||
• supply and demand diagrams to show tariffs, quotas and subsidies.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*Tariff:关税,也称为customs duties,是针对进口品或出口品征收的税收,一般多讨论对进口品收税以提高进口品价格。 | *Tariff:关税,也称为customs duties,是针对进口品或出口品征收的税收,一般多讨论对进口品收税以提高进口品价格。 | ||
**Tariff的常见图像如下: | **Tariff的常见图像如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.2.2-1.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.2.2-1.png |450px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
**关税的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。 | **关税的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。 | ||
| 第175行: | 第186行: | ||
*Quota:(进口)限额,指对进口额度进行严格限制,只允许一定数量的进口品进入该国经济。 | *Quota:(进口)限额,指对进口额度进行严格限制,只允许一定数量的进口品进入该国经济。 | ||
**Quota的常见图像如下: | **Quota的常见图像如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.2.2-2.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.2.2-2.png |450px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
**限额的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。 | **限额的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。 | ||
| 第182行: | 第193行: | ||
*Export subsidies:出口补贴,指对出口企业或本国企业发放一定福利,主要致力于降低出口的生产成本,从而降低价格,使得出口品在国际市场上具有竞争力。同时,也可以鼓励企业多生产商品,占据更多国内市场份额。(国际和国内的市场份额都会上升) | *Export subsidies:出口补贴,指对出口企业或本国企业发放一定福利,主要致力于降低出口的生产成本,从而降低价格,使得出口品在国际市场上具有竞争力。同时,也可以鼓励企业多生产商品,占据更多国内市场份额。(国际和国内的市场份额都会上升) | ||
**export subsidies的常见图像如下: | **export subsidies的常见图像如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.2.2-3.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.2.2-3.png |450px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
**补贴的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。 | **补贴的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。 | ||
| 第193行: | 第204行: | ||
===d) Modern trading blocs: 现代贸易集团=== | ===d) Modern trading blocs: 现代贸易集团=== | ||
• impact of trading blocs on member and non-member countries | {{color|grey| | ||
• examples of trading blocs. | • impact of trading blocs on member and non-member countries<br/> | ||
• examples of trading blocs.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*Trading bloc:贸易集团。指的是区域范围内的一些国家通过成员国间的正式贸易条约联合在一起的团体。 | *Trading bloc:贸易集团。指的是区域范围内的一些国家通过成员国间的正式贸易条约联合在一起的团体。 | ||
| 第202行: | 第214行: | ||
***注意:仅仅是成员国之间取消贸易限制,各成员国与其他非成员国之间的贸易限制不受影响,具体的限制手段和门槛高低都不做额外要求。 | ***注意:仅仅是成员国之间取消贸易限制,各成员国与其他非成员国之间的贸易限制不受影响,具体的限制手段和门槛高低都不做额外要求。 | ||
***free trade area的示意图如下: | ***free trade area的示意图如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-11.6.2-1.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-11.6.2-1.png |300px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
***A国和B国组成了free trade area。两国间的关税为0,但A国使用美元,对非成员国C国的关税是a%;B国使用人民币,对非成员国C国的关税是b%。 | ***A国和B国组成了free trade area。两国间的关税为0,但A国使用美元,对非成员国C国的关税是a%;B国使用人民币,对非成员国C国的关税是b%。 | ||
| 第209行: | 第221行: | ||
***注意:关税同盟在自由贸易区的基础上,增加了common external tariff on imports from non-members对非成员国的进口产品实行统一对外关税的要求。这是关税同盟的最大特点。 | ***注意:关税同盟在自由贸易区的基础上,增加了common external tariff on imports from non-members对非成员国的进口产品实行统一对外关税的要求。这是关税同盟的最大特点。 | ||
***customs union的示意图如下: | ***customs union的示意图如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-11.6.2-2.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-11.6.2-2.png |300px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
****A国和B国组成了customs union。两国间的关税为0,两国对非成员国C国的关税都是a%。但A国使用美元,B国使用人民币。 | ****A国和B国组成了customs union。两国间的关税为0,两国对非成员国C国的关税都是a%。但A国使用美元,B国使用人民币。 | ||
| 第218行: | 第230行: | ||
***注意:有些monetary union仅限于使用同一种货币,并没有更深入的合作,比如一些拉美国家。但也有些monetary union不仅使用了同一种货币,而且在关税同盟的基础上,增加了capital与labour也可以自由流通的要求,体现了更加深入的经济合作。为了管理各国已经统一的货币,团体会成立一个共同的央行来管理该货币并调节相应的货币政策,各国政府不再介入货币政策的管理和调整。 | ***注意:有些monetary union仅限于使用同一种货币,并没有更深入的合作,比如一些拉美国家。但也有些monetary union不仅使用了同一种货币,而且在关税同盟的基础上,增加了capital与labour也可以自由流通的要求,体现了更加深入的经济合作。为了管理各国已经统一的货币,团体会成立一个共同的央行来管理该货币并调节相应的货币政策,各国政府不再介入货币政策的管理和调整。 | ||
***monetary union的示意图如下: | ***monetary union的示意图如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-11.6.2-3.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-11.6.2-3.png |300px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
****A国和B国组成了monetary union。两国间的关税为0,两国对非成员国C国的关税都是a%,且两国均使用美元。 | ****A国和B国组成了monetary union。两国间的关税为0,两国对非成员国C国的关税都是a%,且两国均使用美元。 | ||
| 第240行: | 第252行: | ||
***合作过于深入,可能会引起一些民众不满。统一的政策、法律或文化也可能会影响到本国经济政治环境。 | ***合作过于深入,可能会引起一些民众不满。统一的政策、法律或文化也可能会影响到本国经济政治环境。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===e) Role of the World Trade Organization (WTO): 国际贸易组织的角色=== | ===e) Role of the World Trade Organization (WTO): 国际贸易组织的角色=== | ||
• actions by the WTO. | {{color|grey| | ||
• actions by the WTO.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*World Trade Organization(WTO):世界贸易组织,前身是GATT关贸总协定。其成立的主要目的原本是用于稳定二战后的世界经济与贸易形势,现已转变为维持国际贸易秩序的国际性组织。 | *World Trade Organization(WTO):世界贸易组织,前身是GATT关贸总协定。其成立的主要目的原本是用于稳定二战后的世界经济与贸易形势,现已转变为维持国际贸易秩序的国际性组织。 | ||
| 第256行: | 第270行: | ||
**It is causing hardship for poorer nations. 使得穷国处境更加艰难。 | **It is causing hardship for poorer nations. 使得穷国处境更加艰难。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===f) Trade patterns of developed and developing countries. 发达国家与发展中国家的贸易格局=== | ===f) Trade patterns of developed and developing countries. 发达国家与发展中国家的贸易格局=== | ||
*Patterns of trade:贸易格局,主要体现在以下几个方面: | *Patterns of trade:贸易格局,主要体现在以下几个方面: | ||
| 第280行: | 第295行: | ||
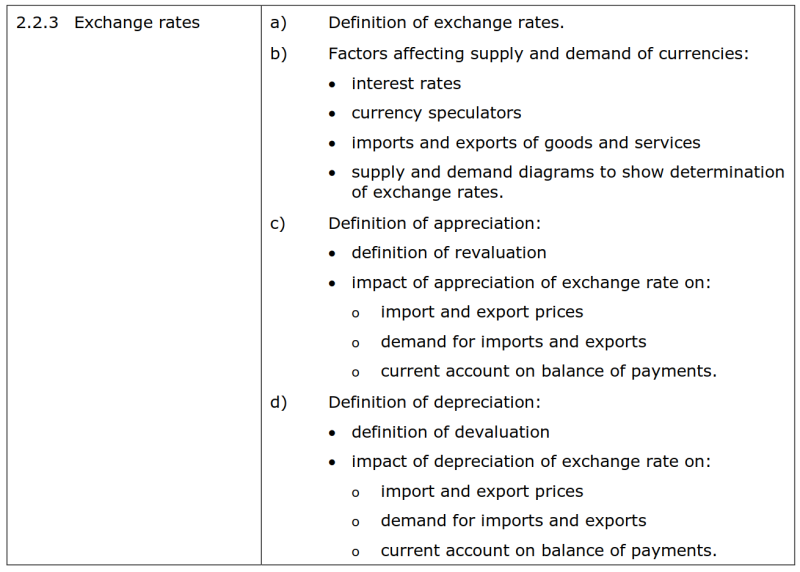
==2.2.3 Exchange rates 汇率== | ==2.2.3 Exchange rates 汇率== | ||
*{{color|red| | *{{color|red|'''大纲要求'''}} | ||
[[File:EdexcelIG2019-2.2.3要求.png|800px]] | [[File:EdexcelIG2019-2.2.3要求.png|800px]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| 第288行: | 第303行: | ||
*Exchange rate:汇率,两种货币的兑换比率,可以看作是用另一国货币来表示本国货币的价值。如果把钱看作是一种特殊商品,那么exchange rate就是一国货币的价格(外部)。 | *Exchange rate:汇率,两种货币的兑换比率,可以看作是用另一国货币来表示本国货币的价值。如果把钱看作是一种特殊商品,那么exchange rate就是一国货币的价格(外部)。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===b) Factors affecting supply and demand of currencies:货币需求与供给的影响因素=== | ===b) Factors affecting supply and demand of currencies:货币需求与供给的影响因素=== | ||
• interest rates | {{color|grey| | ||
• currency speculators | • interest rates<br/> | ||
• imports and exports of goods and services | • currency speculators<br/> | ||
• supply and demand diagrams to show determination of exchange rates. | • imports and exports of goods and services<br/> | ||
• supply and demand diagrams to show determination of exchange rates.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*货币市场同样具有demand和supply,遵循微观学过的供求曲线变化的规律。当demand或supply变化时,均衡点发生变化,汇率也跟着发生波动。 | *货币市场同样具有demand和supply,遵循微观学过的供求曲线变化的规律。当demand或supply变化时,均衡点发生变化,汇率也跟着发生波动。 | ||
| 第311行: | 第328行: | ||
**demand需求线与supply供给线发生变化的图像表示:【参考2.2.3(c)和2.2.3(d)】。 | **demand需求线与supply供给线发生变化的图像表示:【参考2.2.3(c)和2.2.3(d)】。 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
===c) Definition of appreciation: 升值的定义=== | ===c) Definition of appreciation: 升值的定义=== | ||
• definition of revaluation | {{color|grey| | ||
• impact of appreciation of exchange rate on: | • definition of revaluation<br/> | ||
• impact of appreciation of exchange rate on:<br/> | |||
o import and export prices<br/> | |||
o demand for imports and exports<br/> | |||
o current account on balance of payments.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*Floating exchange rate:浮动汇率,指通过市场力(供求关系)来决定的汇率。 | *Floating exchange rate:浮动汇率,指通过市场力(供求关系)来决定的汇率。 | ||
| 第327行: | 第346行: | ||
***Demand上升(下图右) | ***Demand上升(下图右) | ||
**appreciation常见图像如下: | **appreciation常见图像如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.4.3-1.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.4.3-1.png |400px]] [[File: CAIE2023-6.4.3-2.png |400px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| 第338行: | 第357行: | ||
===d) Definition of depreciation: 贬值的定义=== | ===d) Definition of depreciation: 贬值的定义=== | ||
• definition of devaluation | {{color|grey| | ||
• impact of depreciation of exchange rate on: | • definition of devaluation<br/> | ||
• impact of depreciation of exchange rate on:<br/> | |||
o import and export prices<br/> | |||
o demand for imports and exports<br/> | |||
o current account on balance of payments.<br/>}} | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
*depreciation贬值/devaluation法定贬值:exchange rate下降,表现为本币变得不再那么值钱,会换来更少的外币。 | *depreciation贬值/devaluation法定贬值:exchange rate下降,表现为本币变得不再那么值钱,会换来更少的外币。 | ||
| 第350行: | 第370行: | ||
***Demand下降(下图右) | ***Demand下降(下图右) | ||
**depreciation常见图像如下: | **depreciation常见图像如下: | ||
<center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.4.3-3.png | | <center>[[File: CAIE2023-6.4.3-3.png |400px]] [[File: CAIE2023-6.4.3-4.png |400px]]</center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
2023年7月11日 (二) 00:54的最新版本
如遇到公式加载异常,请刷新页面!
2.2 The global economy 全球经济
2.2.1 Globalisation 全球化
- 大纲要求
a) Definition of globalisation: increased integration and interdependence of economies. 全球化的定义
- Globalisation:全球化。指的是全世界逐渐通过贸易、跨国投资等方式联系在一起的过程。
- 全球化的主要特征:
- Goods and services are traded freely across international borders. 商品和服务可以进行自由贸易。
- People are free to live and work in any country they choose. 人们可以在国际间自由往来。
- There is a high level of interdependence between nations. 国家间关系紧密。
- Capital can flow between different countries. 资本(资金)可以在国际间自由往来。
- There is a free exchange of technology and intellectual property across borders. 技术和知识产权可以在国际间自由往来。
- 全球化的主要特征:
b) Reasons for globalisation: 全球化的原因
• fewer tariffs and quotas
• reduced cost of transport
• reduced cost of communication
• increased significance of multinational corporations (MNCs).
- 全球化的原因:
- fewer tariffs and quotas关税下降,贸易限额提升:贸易保护措施的减少,有助于各国之间的商品和服务流动,增加各国之间的贸易往来。
- reduced cost of transport运输成本下降:运输成本降低,有利于商品和服务销往海外市场,也有利于企业从海外购买更便宜的原材料和能源,节约成本。
- reduced cost of communication通讯成本下降:通讯成本降低,各地之间的联络变得更加频繁,有利于进出口的发展。
- increased significance of multinational corporations (MNCs) 跨国公司的重要性:跨国公司数量的上升,有助于各国之间的商品和服务的流动,促进各国之间的联系。
c) Impacts of globalisation and global companies on individual countries, governments, producers and consumers, workers and the environment: 全球化的影响及国际企业对单个国家、政府、生产者与消费者、工人和环境的影响
• rising living standards
• greater choice
• lower prices
• reduced costs of communication
• closing of traditional industries
• environmental impact.
- 全球化的影响:
- rising living standards生活质量提升
- 全球化带来经济增长(尤其是发展中国家的export-led economic growth出口导向型经济增长),提高人们的生活质量。
- greater choice消费者的选择增加
- lower prices商品价格下降(竞争加剧导致)
- reduced costs of communication通讯交流成本降低
- assist local suppliers帮助当地的供应商,增加就业
- Access to huge markets获得更大的市场
- Reduced taxation for firms企业可以减少税收支出(前往低税国生产)
- more tax revenue for the government为政府带来更多税收收入(企业利润增加导致)
- closing of traditional industries传统行业逐渐衰落(竞争不占优势),失业增加
- environmental impact全球化对环境有一定影响。技术的进步和交流可能会改善环境,但大量交通工具的使用、生产扩张也会导致大量污染物排放,污染环境。跨国公司可能会大量消耗当地的资源,导致资源枯竭。
- rising living standards生活质量提升
d) Definition of multinational corporations (MNCs): 跨国公司的定义
• definition of foreign direct investment (FDI)
• reasons for emergence of MNCs/FDI:
o to benefit from economies of scale
o to access natural resources/cheap materials
o lower transport and communication costs
o to access customers in different regions.
• advantages and disadvantages of MNCs/ FDI:
o creating jobs
o investing in infrastructure
o developing skills
o developing capital
o contributing to taxes
o avoiding paying taxes
o environmental damage
o moving profits abroad.
- Foreign direct investment(FDI):外国直接投资。指的是在外国建厂生产或购买外国当地企业,这会给当地带来capital flows资金流。
- Multinational company(MNC):跨国公司。指的是在多个国家运营的公司,除了在本国有母公司之外,在世界其他很多国家或地区(至少一个)都开有分公司。
- 跨国公司常见的特征:
- Huge assets and revenue:大量的资产与收入
- Highly qualified and experienced professional executives and managers:高素质、有经验的专业经理人
- Powerful advertising and marketing capability:强有力的广告与市场营销能力
- Highly advanced and up-to-date technology:高度先进的技术
- Highly influential both economically and politically:在经济与政治上能够施加高度影响力
- Very efficient since they can exploit huge economies of scale:能够享受大量规模经济,效率高
- 跨国公司常见的特征:
- 外国直接投资FDI和跨国公司MNC出现的原因:
- benefit from economies of scale能够享受到规模经济。
- access natural resources/cheap materials获取当地的自然资源或廉价原材料。
- lower transport and communication costs更低的运输和交流成本。
- access customers in different regions接触到不同地区的市场和消费者。
- 外国直接投资FDI和跨国公司MNC的优缺点:
- creating jobs创造就业方面:FDI和MNC引进后,对当地劳动力的需求增加,能够解决当地的失业问题,且由于跨国公司提供工资水平一般高于当地平均水平,工人能够增加收入。但如果当地企业因为难以与跨国公司竞争而倒闭,也会增加失业。
- investing in infrastructure投资基建方面:政府为吸引外国投资,会完善和修建基础设施。在FDI和MNC引进后,这些企业也可能会为当地修建一些基础设施(如公路、路灯等),以方便产品和原料运输,顺便也提升了当地人们的生活水平。但有时为了建工厂,也会拆除一些基建,影响人们生活。
- developing skills技能提升方面:FDI和MNC引进后,会参与培训当地劳动力,和当地就业者进行技术、管理方面的交流,提高当地的技术、管理能力。政府为了吸引投资,也会重视教育和培训。
- developing capital资本发展方面:FDI和MNC引进后,带来充足的资本用以投资和技术研发,也鼓励和带动当地企业生产和创新,能够促进当地经济增长。
- contributing to taxes税收方面:FDI和MNC引进后,可以为当地提供大量税收,改善当地财政情况。
- avoiding paying taxes:避税方面:MNC有时会向政府故意瞒报自身盈利情况以避税,增加了当地的监管难度。
- environmental damage环境方面:MNC在当地生产时,会消耗大量当地的资源,同时也会排放大量污染物,破坏当地自然环境。但有时MNC也会带来先进的污染处理技术,改善当地环境。
- moving profits abroad利润回流方面:MNC可能会通过一些方式将所赚利润转移到母公司所在国家,并不留在当地帮助当地发展经济。这会导致资金流出本国,影响本国经济增长。
2.2.2 International trade 国际贸易
- 大纲要求
a) Advantages and disadvantages of free trade, including: 自由贸易的优缺点
• lower prices and increased choice for consumers
• lower input costs
• wider markets for businesses
• foreign competition harming domestic businesses
• increasing unemployment.
- Free trade:自由贸易,即没有贸易壁垒,市场可以自由决定进出口的数量和种类。
- 国际贸易的目的:
- Obtaining goods that cannot be produced domestically. 获取本国无法生产的产品
- Obtaining goods that can be bought more cheaply from overseas. 获取比本国更便宜的商品
- Selling off unwanted commodities. 卖出不需要的商品
- 国际贸易的目的:
- Free trade 自由贸易的影响:
- lower prices and increased choice for consumers价格下降,消费者的选择增加(竞争增加导致)。
- lower input costs原材料成本下降(企业可以选择进口海外更便宜的原材料)。
- wider markets for businesses更大的市场,产品可以卖到世界各地。
- foreign competition harming domestic businesses外部竞争会对本国企业造成危害。自由贸易后,市场竞争加剧,如果本国企业无法与外国企业抗衡,就会面临倒闭的危机。
- increasing unemployment失业增加(本国企业倒闭或国际贸易格局改变导致)。
- Vulnerability经济更加脆弱,依赖性强,容易受到外界冲击。
b) Reasons for protection: 贸易保护的原因
• prevent dumping
• protect employment
• protecting infant industries
• to gain tariff revenue
• protect consumers from unsafe products
• reducing current account deficits
• retaliation
- Protectionism:贸易保护主义。通过一系列政策强制干预正常贸易,设置trade barriers贸易门槛,达到减少进口或增加出口的目的。
- 贸易保护的原因:
- To protect infant (sunrise) industries保护朝阳行业
- 为刚刚成立的小企业营造一个相对利于成长的环境,减少竞争压力,等到其具有和国际企业抗衡的资本(economies of scale或international reputation)后再去掉壁垒。
- To protect declining (sunset) industries保护夕阳行业
- 为避免被时代淘汰的企业大量倒闭带来的大量失业,通过壁垒延缓其倒闭速度,给失业人群和经济一个缓冲期。
- To protect strategic industries保护战略性行业
- 一些攸关国家战略安全的行业(如武器、农业、能源等),不能全部依赖进口,即使没有生产优势也要设置壁垒来降低进口、增加本国的产量。
- To prevent dumping阻止倾销
- 对外国的dumping倾销行为进行反倾销,征收惩罚性关税,保障本国企业合法利益。
- To improve the balance of payments改善国际收支账户
- 通过贸易保护的各种手段,增加了出口或降低了进口,使得贸易逆差trade deficit下降(或贸易顺差surplus上升)。
- To protect employment保护就业
- 通过贸易保护,减少外国企业对本国企业造成的竞争压力,避免本国企业倒闭,保护本国就业。
- To gain tariff revenue获得税收收益
- 通过收取关税,增加本国政府税收收入。
- To protect consumers from unsafe products保护消费者,阻止不安全的商品
- 通过贸易保护,阻止不合格产品进入本国,可以保护本国消费者的合法利益和生命安全。
- Retaliation报复
- 如果外国对本国实施了贸易保护,本国也可以对外国实施贸易保护以反制。
- To protect infant (sunrise) industries保护朝阳行业
c) Methods of protection: 贸易保护的方式
• tariffs
• quotas
• subsidies
• advantages and disadvantages of each method of protection
• supply and demand diagrams to show tariffs, quotas and subsidies.
- Tariff:关税,也称为customs duties,是针对进口品或出口品征收的税收,一般多讨论对进口品收税以提高进口品价格。
- Tariff的常见图像如下:
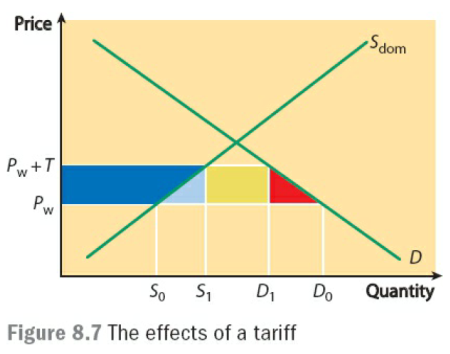
- 关税的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。
- 关税的问题:
- 减少自由贸易及其带来的各项好处。
- 消费者的选择减少。
- 生产者难以选择国外的廉价原材料和能源,生产成本上升。
- 本国生产者缺少竞争,没有动力研发和降低成本,生产效率下降。
- Quota:(进口)限额,指对进口额度进行严格限制,只允许一定数量的进口品进入该国经济。
- Quota的常见图像如下:
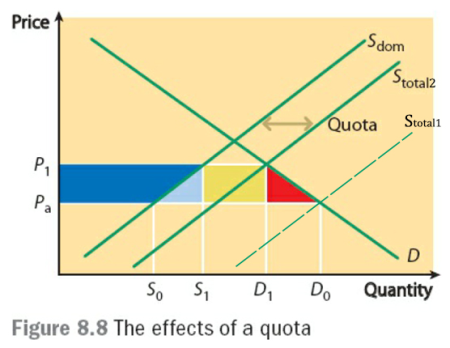
- 限额的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。
- 限额的问题:参考上面关税的问题。
- Export subsidies:出口补贴,指对出口企业或本国企业发放一定福利,主要致力于降低出口的生产成本,从而降低价格,使得出口品在国际市场上具有竞争力。同时,也可以鼓励企业多生产商品,占据更多国内市场份额。(国际和国内的市场份额都会上升)
- export subsidies的常见图像如下:
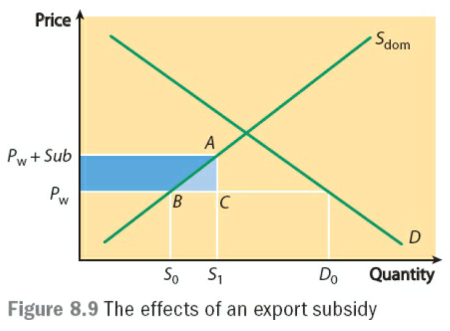
- 补贴的好处:参考上面有关“贸易保护的原因”部分。
- 补贴的问题:
- 减少自由贸易及其带来的各项好处。
- 降低生产效率。
- 大量发放补贴,增加财政压力。
- 国家发放补贴,容易被认定为dumping倾销。Dumping是商品售卖价格低于生产成本的情况,属于故意扰乱市场的行为。一旦其他国家被认定存在dumping,将被征收非常重的惩罚性关税,会直接导致该商品退出认定国的市场。
d) Modern trading blocs: 现代贸易集团
• impact of trading blocs on member and non-member countries
• examples of trading blocs.
- Trading bloc:贸易集团。指的是区域范围内的一些国家通过成员国间的正式贸易条约联合在一起的团体。
- Trading bloc的主要类型及特点:
- Preferential trading areas(PTA):优惠贸易区。指的是成员国之间同意取消一部分商品与服务的关税的团体。
- free trade area(FTA):自由贸易区。指的是成员国之间相互取消贸易限制的团体。
- 注意:仅仅是成员国之间取消贸易限制,各成员国与其他非成员国之间的贸易限制不受影响,具体的限制手段和门槛高低都不做额外要求。
- free trade area的示意图如下:
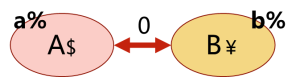
- A国和B国组成了free trade area。两国间的关税为0,但A国使用美元,对非成员国C国的关税是a%;B国使用人民币,对非成员国C国的关税是b%。
- 常见的free trade area自由贸易区例子有:美加墨自由贸易区(USMCA)
- customs union:关税同盟。指的是成员国之间相互取消贸易限制,并对其他非成员国的进口产品实行统一的对外关税的团体。
- 注意:关税同盟在自由贸易区的基础上,增加了common external tariff on imports from non-members对非成员国的进口产品实行统一对外关税的要求。这是关税同盟的最大特点。
- customs union的示意图如下:
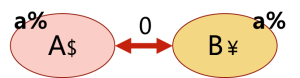
- A国和B国组成了customs union。两国间的关税为0,两国对非成员国C国的关税都是a%。但A国使用美元,B国使用人民币。
- 常见的customs union关税同盟的例子有:南部非洲关税同盟(SACU)
- Common market:共同市场。指的是成员国之间劳动力和资本也可以自由流动的团体。
- monetary union:货币同盟,也可以理解为economic union经济同盟。指的是成员国间使用同一种货币、同一货币政策甚至是更深入合作的团体。
- 注意:货币同盟要求各国使用同一种货币。因为使用了同一种货币,因此货币的汇率和利率也应该相同。这些国家将采取同样的货币政策与利率政策。
- 注意:有些monetary union仅限于使用同一种货币,并没有更深入的合作,比如一些拉美国家。但也有些monetary union不仅使用了同一种货币,而且在关税同盟的基础上,增加了capital与labour也可以自由流通的要求,体现了更加深入的经济合作。为了管理各国已经统一的货币,团体会成立一个共同的央行来管理该货币并调节相应的货币政策,各国政府不再介入货币政策的管理和调整。
- monetary union的示意图如下:
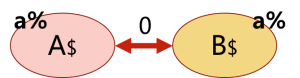
- A国和B国组成了monetary union。两国间的关税为0,两国对非成员国C国的关税都是a%,且两国均使用美元。
- 常见的monetary union货币同盟的例子有:欧盟(EU)
- monetary union货币同盟存在的问题:
- 各国无法再使用独立的monetary policies和exchange rate policies调节自己国家的经济。而统一央行做出的调节可能和国内情况不符,加剧国内经济的恶化。所以有时候一些国家会选择退出monetary union货币同盟以实现重新实施独立monetary policy和exchange rate policy的自由。
- 贸易集团的影响:
- 好处:
- 关税的去除会降低商品价格。
- 消费者选择更多。
- 自由贸易带来出口导向型经济增长。
- 企业面临更广大的市场,可以扩大生产规模,享受economies of scale规模经济,降低生产平均成本。
- 引入FDI外国投资更加方便,更容易交流技术、管理经验等。
- 减少贸易争端。
- 问题:
- Trade bloc为非成员国设置了较高门槛,影响世界范围内的自由贸易。
- 成员国需要向组织缴纳一定资金,增加成员国的财政压力。
- 容易出现monopoly垄断企业,降低竞争与效率。
- 太过依赖贸易,经济脆弱,容易受到外部冲击。
- 合作过于深入,可能会引起一些民众不满。统一的政策、法律或文化也可能会影响到本国经济政治环境。
- 好处:
e) Role of the World Trade Organization (WTO): 国际贸易组织的角色
• actions by the WTO.
- World Trade Organization(WTO):世界贸易组织,前身是GATT关贸总协定。其成立的主要目的原本是用于稳定二战后的世界经济与贸易形势,现已转变为维持国际贸易秩序的国际性组织。
- WTO的作用:
- Trade negotiations贸易协商
- Implementation and monitoring实施和监督贸易规则
- Settling trade disputes解决贸易争端
- Building membership鼓励成员国加入
- 对WTO的批评:
- It is undemocratic不够民主,仅站在企业的角度看问题。
- It favours the rights' of corporations over those of workers. 将企业利益置于工人利益之上。
- It is destroying the environment. 可能危害环境。
- It favours wealthy nations over poorer ones. 比起穷国更注重富国。
- It is causing hardship for poorer nations. 使得穷国处境更加艰难。
f) Trade patterns of developed and developing countries. 发达国家与发展中国家的贸易格局
- Patterns of trade:贸易格局,主要体现在以下几个方面:
- Increase in world trade世界贸易增加
- 原因:
- Better transport and communications更好的交通和交流条件
- Relaxing of trade barriers贸易门槛的降低
- Development of multinationals跨国公司的发展
- Travel and consumer awareness旅游和消费者意识
- Trade agreements贸易协议
- 原因:
- Trade in developed countries发达国家的交易
- 特征:
- Loss of trade in manufacturing下降的制造品交易(制造业已经转移)
- More air travel更多的航空旅行
- Widening of the development gap发展陷阱越来越严重
- 特征:
- Trade in developing countries发展中国家的贸易
- 特征:
- An increase in net migration净移民的增加(移往发达国家)
- Increased FDI in Africa对非洲国家的对外投资增加
- Rise in commodity dependence大宗商品依赖增强(仅出口初级产品)
- Debt cancellation债务取消
- Reduction in barriers门槛下降
- 特征:
- Increase in world trade世界贸易增加
2.2.3 Exchange rates 汇率
- 大纲要求
a) Definition of exchange rates. 汇率的定义
- Exchange rate:汇率,两种货币的兑换比率,可以看作是用另一国货币来表示本国货币的价值。如果把钱看作是一种特殊商品,那么exchange rate就是一国货币的价格(外部)。
b) Factors affecting supply and demand of currencies:货币需求与供给的影响因素
• interest rates
• currency speculators
• imports and exports of goods and services
• supply and demand diagrams to show determination of exchange rates.
- 货币市场同样具有demand和supply,遵循微观学过的供求曲线变化的规律。当demand或supply变化时,均衡点发生变化,汇率也跟着发生波动。
- 货币市场的demand需求表现为外国是否大量需要本国货币,主要源自:
- Interest rates利率。
- 高利率会吸引hot money热钱大量流入,增加货币需求。
- Currency speculators货币投机。
- 如果人们预计货币未来会升值,则会增加货币需求,以便未来高价卖出赚取差价。
- The demand for exports出口需求。
- 外国购买出口品时需要支付本国货币,因此会增加对本币的需求。
- Interest rates利率。
- 货币市场的supply供给表现为本国是否大量提供本国货币,主要源自:
- Interest rates in other countries其他国家利率。
- 其他国家利率高,hot money会卖出大量本币以离开本国,前往其他国家获利。
- Currency speculators货币投机。
- 如果人们预计货币未来会贬值,则会大量卖出货币以减少损失。
- The demand for imports进口需求。
- 本国购买进口品时需要提供本国货币以换取外币,从而购买外国商品。
- Interest rates in other countries其他国家利率。
- demand需求线与supply供给线发生变化的图像表示:【参考2.2.3(c)和2.2.3(d)】。
- 货币市场的demand需求表现为外国是否大量需要本国货币,主要源自:
c) Definition of appreciation: 升值的定义
• definition of revaluation
• impact of appreciation of exchange rate on:
o import and export prices
o demand for imports and exports
o current account on balance of payments.
- Floating exchange rate:浮动汇率,指通过市场力(供求关系)来决定的汇率。
- Fixed exchange rate:固定汇率,指政府规定的汇率。
- appreciation升值/revaluation法定升值:exchange rate上升,表现为本币更加值钱,能换来更多的外币。
- 注意:appreciation是升值在浮动汇率下的表述,revaluation是升值在固定汇率下的表述。
- 货币出现appreciation的情况:
- Supply下降(下图左)
- Demand上升(下图右)
- appreciation常见图像如下:
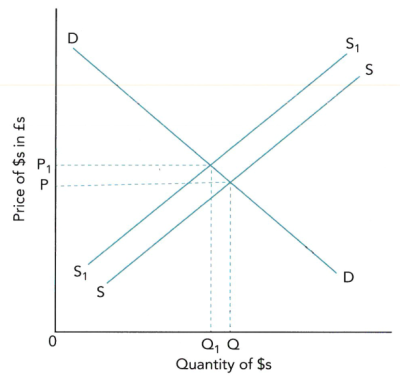
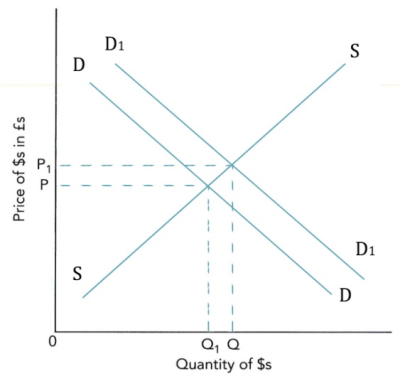
- 货币升值的影响:
- 对import and export prices进出口价格:货币升值会导致出口价格上升,进口价格下降。
- 对demand for imports and exports进出口需求:货币升值,出口价格上升,出口下降;进口价格下降,进口增加。
- 注意:对进出口的影响与PED有关。如果进出口的商品是inelastic缺乏弹性的,则出口价格的上升会导致出口增加,进口价格的下降会导致进口下降。
- 对current account on balance of payments经常账户:货币升值后出口下降,进口增加,容易出现current account deficit经常账户逆差。
d) Definition of depreciation: 贬值的定义
• definition of devaluation
• impact of depreciation of exchange rate on:
o import and export prices
o demand for imports and exports
o current account on balance of payments.
- depreciation贬值/devaluation法定贬值:exchange rate下降,表现为本币变得不再那么值钱,会换来更少的外币。
- 注意:depreciation是升值在浮动汇率下的表述,devaluation是升值在固定汇率下的表述。
- 货币出现depreciation的情况:
- Supply上升(下图左)
- Demand下降(下图右)
- depreciation常见图像如下:
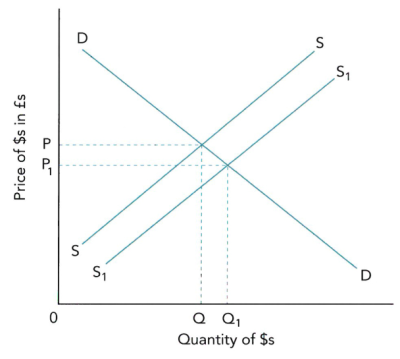
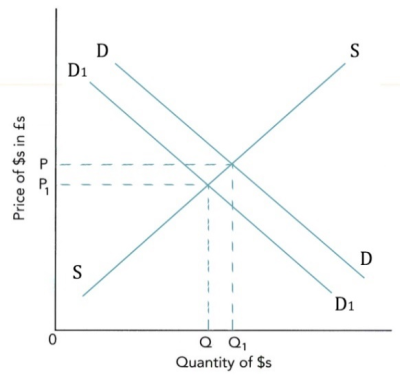
- 货币贬值的影响:
- 对import and export prices进出口价格:货币贬值会导致出口价格下降,进口价格上升。
- 对demand for imports and exports进出口需求:货币贬值,出口价格下降,出口上升;进口价格上升,进口下降。
- 注意:对进出口的影响与PED有关。如果进出口的商品是inelastic缺乏弹性的,则出口价格的下降会导致出口下降,进口价格的上升会导致进口增加。
- 对current account on balance of payments经常账户:货币贬值后出口上升,进口下降,容易出现current account surplus经常账户顺差。