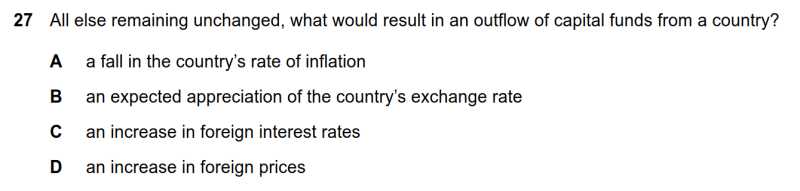来自A level and IG Revision Wiki
跳到导航
跳到搜索
|
|
| 第1行: |
第1行: |
| | <center><big>[[CAIE AS and A Level past papers|'''【点此返回历年真题目录】''']]</big></center> |
| | <br/> |
| <big>'''单题搜索方法''':右上角搜索中输入'''该题题干中的部分文字''',点击搜索后进入相关页面,然后使用ctrl+F5(或其他按键组合调出搜索框),再次搜索该题干文字,直接定位到题目。</big> | | <big>'''单题搜索方法''':右上角搜索中输入'''该题题干中的部分文字''',点击搜索后进入相关页面,然后使用ctrl+F5(或其他按键组合调出搜索框),再次搜索该题干文字,直接定位到题目。</big> |
| <br/> | | <br/> |
2022年8月15日 (一) 15:27的版本
【点此返回历年真题目录】
单题搜索方法:右上角搜索中输入该题题干中的部分文字,点击搜索后进入相关页面,然后使用ctrl+F5(或其他按键组合调出搜索框),再次搜索该题干文字,直接定位到题目。
整卷下载
试卷难易度分析
试卷难易度分析
| 考察章节 |
容易 |
中等 |
困难 |
总计
|
| Chapter 7 |
7 |
5 |
0 |
12
|
| Chapter 8 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
4
|
| Chapter 9 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
5
|
| Chapter 10 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
3
|
| Chapter 11 |
2 |
4 |
0 |
6
|
| 总计 |
13 |
17 |
0 |
30
|
题目解答
1
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
private/external/social benefit and cost等的概念与计算
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 由于net social value=0,所以social benefit应等于social cost。
● 根据题干及计算公式,能够得出各变量的数值。Private benefit=80;external benefit=20;social benefit=100;private cost=40;external cost=60;social cost=100。根据选项中表述的大小关系,能够得出A选项正确,其他均错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
1 A project has a social cost of $100 million, a private cost of $40 million and an external benefit of $20 million. Its net social value is zero. What can be concluded about the project?
|
2
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
allocative efficiency的判定
|
| 解答要点 |
|
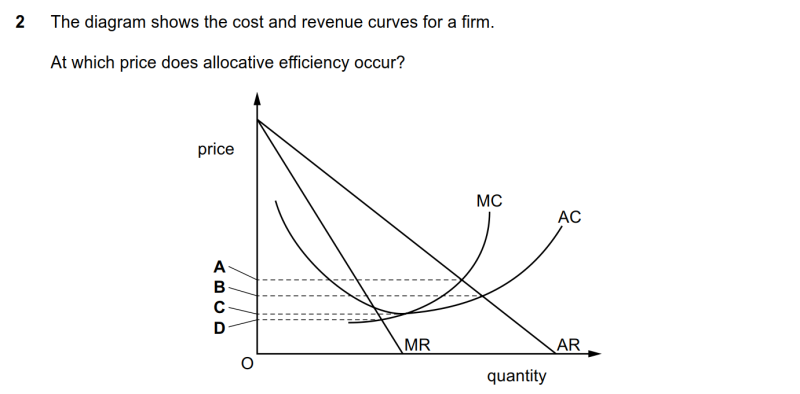
● 根据分配效率的判定公式AR=MC,可以找到两条线的交点,对应的价格为A选项。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
2 The diagram shows the cost and revenue curves for a firm. At which price does allocative efficiency occur?
|
3
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
cost-benefit analysis的运用
|
| 解答要点 |
|
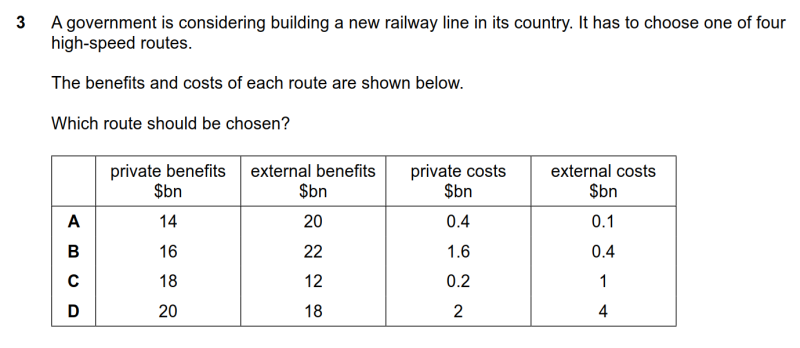
● 根据提供所给的private及external各变量的值,可算出各方案的social cost与social benefit,计算net social benefit = social benefit - social cost,选择最高的方案。即B选项。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
3 A government is considering building a new railway line in its country. It has to choose one of four high-speed routes. The benefits and costs of each route are shown below. Which route should be chosen?
|
4
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
D
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
marginal utility的计算
|
| 解答要点 |
|
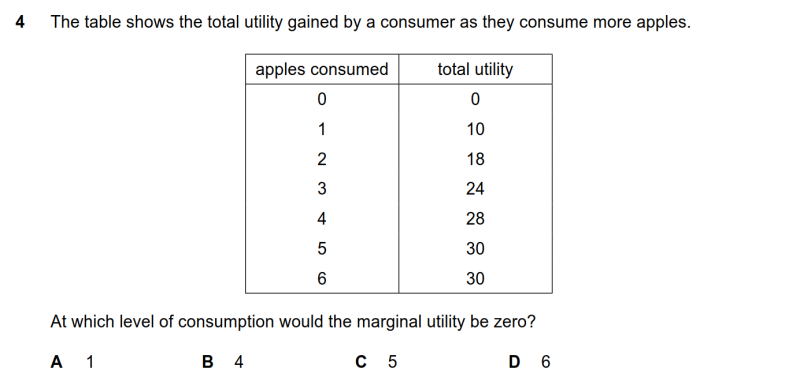
● 根据MU的计算公式:MU=TUx-TUx-1,能够看出从5增加到6时,对应的MU为0,即第6个的MU为0,D选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
4 The table shows the total utility gained by a consumer as they consume more apples. At which level of consumption would the marginal utility be zero?
|
5
| 题目 |
|
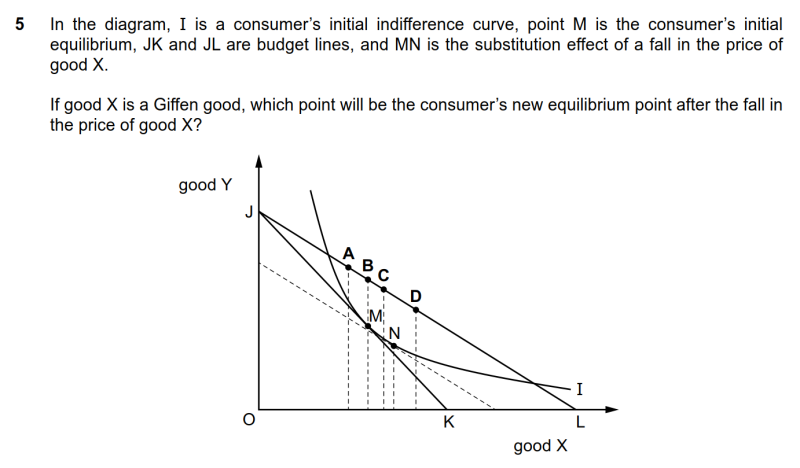
|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
Giffen good的无差异曲线与预算线图像的识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 由于I线为最初的无差异曲线,因此与之相切的JK为初始预算线而JL为后期预算线,预算线的向右旋转意味着价格的下降。
● 最初的无差异曲线I与最初的预算线JK切在M处,因此对应的数量应该为B选项对应的数量。
● Giffen good的特征为价格下降时,需求量也随之下降。因此后期的数量应该在B选项数量的左侧,即A选项是唯一合理的数量位置,A选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
5 In the diagram, I is a consumer’s initial indifference curve, point M is the consumer’s initial equilibrium, JK and JL are budget lines, and MN is the substitution effect of a fall in the price of good X. If good X is a Giffen good, which point will be the consumer’s new equilibrium point after the fall in the price of good X?
|
6
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
D
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
horizontal integration的识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 横向合并为供应链上两个同阶段企业的合并,只有D选项符合要求。
● A选项是混合合并,B选项是纵向合并,C选项是内部增长。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
6 What is an example of horizontal integration?
|
7
| 题目 |
|
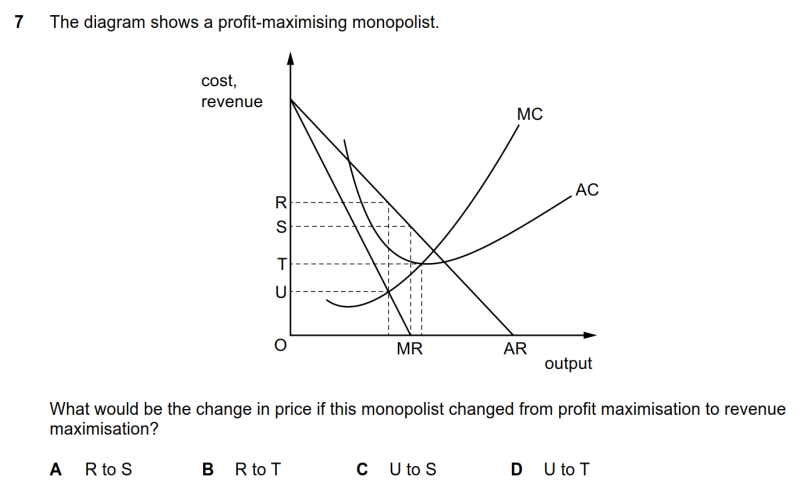
|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
利润最大化与收入最大化的判定与识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● profit maximisation的数量判定式是MR=MC,在该数量上去AC线上找到对应的价格R点。
● revenue maximisation的数量判定式是MR=0,在该数量上去AC线上找到对应的价格S点。
● 价格变化应该为R点到S点,A选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
7 The diagram shows a profit-maximising monopolist. What would be the change in price if this monopolist changed from profit maximisation to revenue maximisation?
|
8
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
satisficing的概念识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 题干中描述的概念是satisficing目标,经理人需要满足股东要求的最低利润水平。B选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
8 The goal of firm X is to make a minimum acceptable level of profit. What does this describe?
|
9
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
D
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
contestable market中垄断市场的特征
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 普通市场下的monopoly在长期可以赚到supernormal profit,只有处于contestable market中时,因为门槛极低,企业为维持市场份额,不得不放弃supernormal profit,主动接受normal profit以阻止其他企业进入该行业。D选项正确。其他选项均不是决定性因素。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
9 A monopoly firm makes only normal profit in the long run. What is most likely to explain this?
|
10
| 题目 |
|
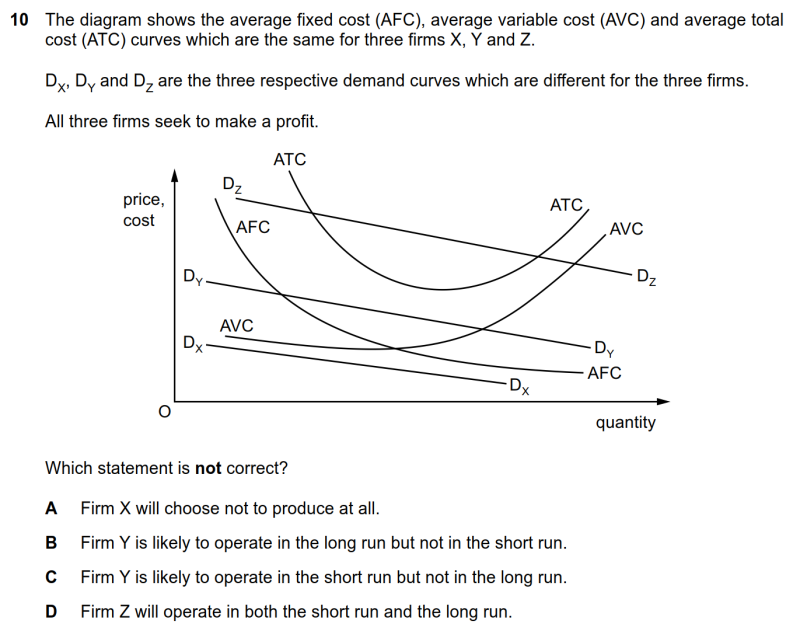
|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
monopolistic market中企业开关门的条件
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● Dz高于ATC,能赚到supernormal profit;Dy高于AVC但低于ATC,短期内亏本继续经营,但长期将选择倒闭;Dx低于AVC,即使短期内也会选择倒闭。
● 综上所述,B选项的内容是不正确的,满足题意,是正确选项。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
10 The diagram shows the average fixed cost (AFC), average variable cost (AVC) and average total cost (ATC) curves which are the same for three firms X, Y and Z. DX, DY and DZ are the three respective demand curves which are different for the three firms. All three firms seek to make a profit. Which statement is not correct?
|
11
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
returns to scale的识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 题干中讨论的是input的变化率与output的变化率之间的关系,因此讨论的应该是returns to scale的概念。Input变化率高于output变化率,因此属于decreasing returns to scale,B选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
11 When a firm increases all its inputs fourfold, its output increases threefold. What does this illustrate?
|
12
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
进入门槛的识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● C选项提到的没有与投资相关的大规模成本,说明成本门槛低,正确。
● A选项是高市场门槛,B选项是高成本门槛,D选项是高法律门槛,与题干不符,均错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
12 Which characteristic of an industry works towards reducing the barriers to entry for new firms?
|
13
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
D
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
negative income tax对平等的影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 从图像上分析可知,高收入人群交税更多(横轴上方部分,NT1高于NT),而低收入人群获得补贴更多(横轴下方部分,NT1低于NT)。这意味着不工作能得到更多的钱,工作赚钱却需要交更多的税,所以人们工作热情较低。但收入差距进一步缩小。因此D选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
13 A country has a negative income tax. The curve NT in the diagram shows the country’s initial tax schedule. A change in the tax rate causes the schedule to shift to NT1. How will this affect work incentives and the after-tax distribution of income?
|
14
| 题目 |
|
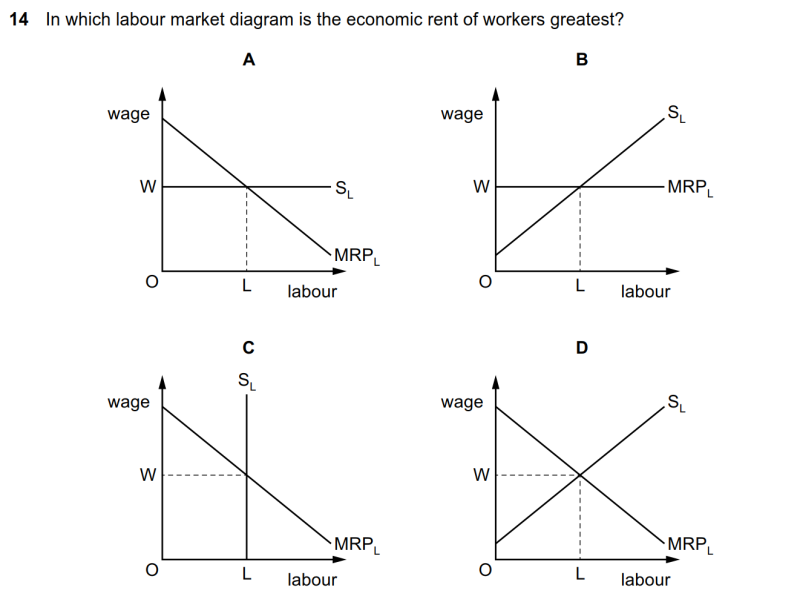
|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
economic rent的图像识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● A选项中没有economic rent,B选项和D选项中的economic rent为W线S线Y轴围出的三角形,C选项中的economic rent为W线下方的长方形。
● 因此C选项中的economic rent最大。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
14 In which labour market diagram is the economic rent of workers greatest?
|
15
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
D
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
minimum wage的影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 高于原市场工资水平的最低工资是有效的,这意味着此时劳动力的供给将大于需求,产生surplus,这部分劳动力将失业,其中包括一些原来有工作的工人,因此D选项符合题意,正确。
● A选项,并非所有员工都会收到新的最低工资,原本工资水平高于最低工资的员工还会按照原工资发放。
● B选项,由于最低工资高于原工资,因此会有更多的劳动力被吸引到该行业,而非更少,B错误。
● C选项,同D选项的解释,此时会用一部分原来用工作的工人失业,所以并非增加,C错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
15 The government introduces a minimum wage above the equilibrium market wage rate. How will this affect low-paid workers according to marginal revenue product (MRP) theory?
|
16
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
quota带来的福利损失
|
| 解答要点 |
|
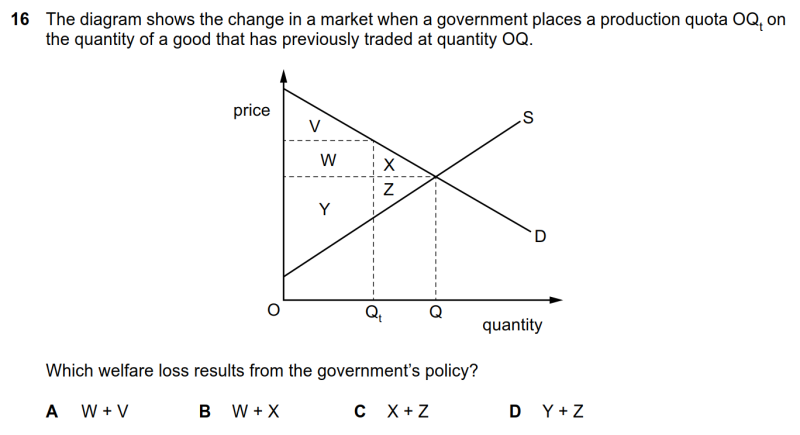
● 由于quota的存在,市场上的产品数量将减少为OQt,价格会抬升。
● 此时consumer surplus由V+W+X减少为V,共损失W+X,但W转移给了生产商作为利润的一部分,实际净损失了X。
● 此时原producer surplus因为产量减少了QQt而损失了Z。
● 因此总的福利损失应为X+Z,C选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
16 The diagram shows the change in a market when a government places a production quota OQt on the quantity of a good that has previously traded at quantity OQ. Which welfare loss results from the government’s policy?
|
17
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
actual和potential economic growth在PPC上的表示
|
| 解答要点 |
|
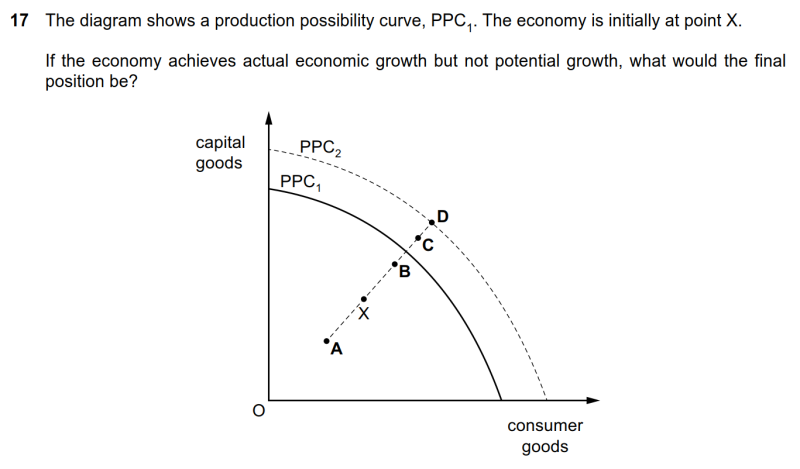
● actual economic growth表现为线内的点向线上靠近,potential economic growth表现为PPC向外扩张。
● 根据题干描述,无potential economic growth意味着线没有外扩,排除C、D。发生了actual economic growth,说明点朝线靠近,因此B正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
17 The diagram shows a production possibility curve, PPC1. The economy is initially at point X. If the economy achieves actual economic growth but not potential growth, what would the final position be?
|
18
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
GDP用于衡量生活质量的局限性
|
| 解答要点 |
|
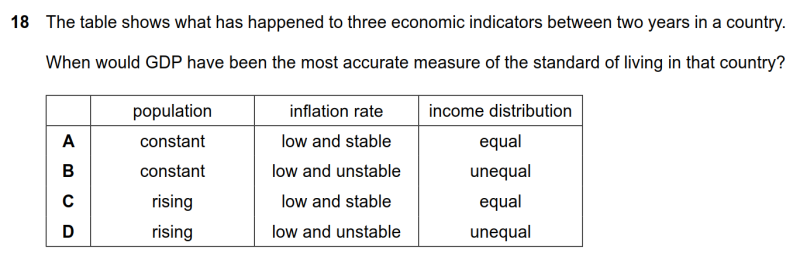
● 表中列出的因素都能够很明显地影响GDP衡量生活质量的精准度,因此要尽量保证这些因素不变。所以人口需要稳定,通胀需要低稳,收入分配需要公平,A选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
18 The table shows what has happened to three economic indicators between two years in a country. When would GDP have been the most accurate measure of the standard of living in that country?
|
19
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
HDI包含的维度
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 四个选项中只有life expectancy是直接包含在HDI维度中,其变化将直接影响HDI,因此B选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
19 Which change would directly affect a country’s Human Development Index (HDI)?
|
20
| 题目 |
|
|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
对失业率的分析
|
| 解答要点 |
|
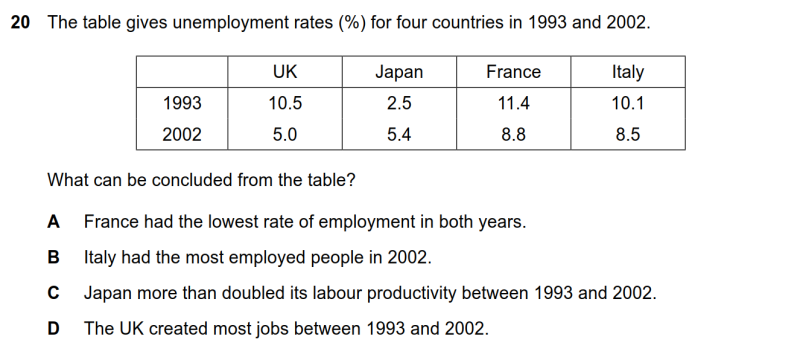
● A选项,法国失业率是四个国家中最高的,大概率其就业率是最低的,A选项正确。
● B选项,2002年意大利的失业率相对较高,因此大概率其就业人口并非最多,B错误。
● C选项,日本失业率翻了一番的原因是多因素造成的,不能单纯归咎于劳动生产率上升2倍,C错误。
● D选项,D选项,与C选项类似,英国失业率下降的原因也是多因素造成,不能单纯归因于工作岗位增加,D错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
20 The table gives unemployment rates (%) for four countries in 1993 and 2002. What can be concluded from the table?
|
21
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
纠正周期性失业的政策
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 周期性失业的原因是AD不足,因此提升AD的政策对其有效。
● 只有C选项能够带来AD的提升,因此C选项正确。A、B、D三个选项均为紧缩型财政政策,带来AD的下降。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
21 A government in a high-income economy wishes to reduce cyclical unemployment. Which policy is likely to be most effective?
|
22
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
Kuznets curve反映的经济问题
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● Kuznets curve表现的是经济增长与收入不平等之间的关系,因此A选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
22 What does the Kuznets curve represent?
|
23
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
乘数的计算
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 根据乘数的计算公式,\(multiplier=\frac{1}{mps+mrt+mpm}=\frac{1}{0.2+0.3+0.3}=1.25\)。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
23 In an open economy with a government sector, the marginal propensity to import is 0.3, the marginal propensity to tax is 0.3 and the marginal propensity to save is 0.2. What is the value of the multiplier?
|
24
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
宏观经济目标之间的冲突与联系
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● A选项,高经济增长容易带来高通胀,包括demand-pull和cost-push两种类型,因此A错误。
● B选项,高经济增长会带来低失业,正确。
● C选项,inflation与unemployment呈反相关关系,低失业代表经济增长较快,容易高通胀。C错误。
● D选项,低失业代表经济增长较快,容易大量进口商品或原材料,贸易容易发生trade deficit,D错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
24 Which macroeconomic policy aims are most likely to complement one another?
|
25
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
B
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
quantitative easing的概念识别
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● quantitative easing指的是央行通过购买商业银行的债券等资产,发放现金等流动性资产的过程,以便为市场提供更多资金发放贷款,增加流动性。与题干描述概念相符,B选项正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
25 The central bank of a country creates cash to purchase government bonds from the commercial banks. What is this called?
|
26
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
A
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
对政府失灵的理解
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● A选项,政府失灵的概念表述为政府的政策会导致net welfare loss,与选项表述一致,A正确。
● B选项,政府的决策也可能存在inefficiency,因此B错误。
● C选项,market来分配资源也会存在market failure,因此C错误。
● D选项,尽管有市场失灵,也不能保证政府一定会使得情况好转,毕竟也存在着政府失灵,因此D错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
26 Which statement about government intervention is correct?
|
27
| 题目 |
|
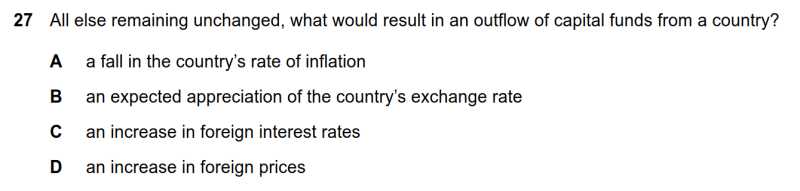
|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
货币市场需求与供给的变化
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● A选项,本国通胀下降,出口将增加,资金会inflow,因此A错误。
● B选项,预期汇率升值,在有预期的情况下,资金基本已经调整到位,因此不太再会引起资金变化,B错误。
● C选项,外国利率上升,这会吸引本国资金前往国外寻求高利率盈利,因此资金会outflow,C正确。
● D选项,外国价格提升,本国会减少进口,资金outflow减少,D错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
27 All else remaining unchanged, what would result in an outflow of capital funds from a country?
|
28
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
贸易保护政策对就业的影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● C选项,通过增加关税,增加贸易保护,减少了进口对本国的冲击,能够保护本国生产企业,进而保护本国就业。C正确。
● A、B、D三个选项均为减少贸易保护的政策,进口增加容易造成本国企业倒闭或缩减规模,失业上升。因此ABD均错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
28 In country X the government aims to protect jobs. Which policy is most likely to succeed?
|
29
| 题目 |
|
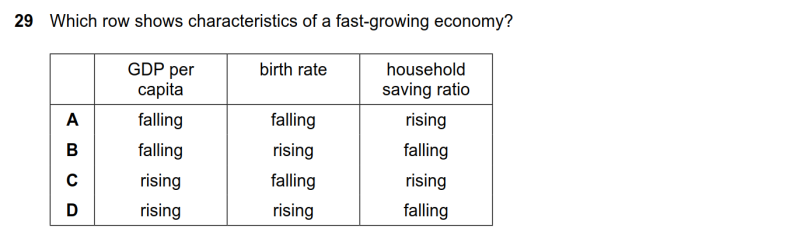
|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
新兴经济体的特征
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 经济增长迅速的经济体拥有上升的人均GDP、出生率逐渐下降(摆脱发展中经济体时期的高出生率情况)和较高的国民储蓄率(收入增加,储蓄上升)。因此C正确。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
29 Which row shows characteristics of a fast-growing economy?
|
30
| 题目 |
|

|
| 答案 |
|
C
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
人均GDP用于衡量生活质量的局限性
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● A选项,该指标全球口径基本相同,可正常用于国际间比较,无需为此调整。A错误。
● B选项,该指标已经使用real value,排除了inflation的影响,无需为此调整,B错误。
● C选项,官方统计的GDP没有考虑一些非法活动等带来的影响,因此会低估国家真实发生的经济活动情况,确实需要考虑hidden economy的规模,C选项正确。
● D选项,出口情况正常包含在GDP中,无需特别关注与调整,D错误。
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
30 Which adjustments to real GDP per capita might make it a more reliable indicator when comparing standards of living in different countries?
|