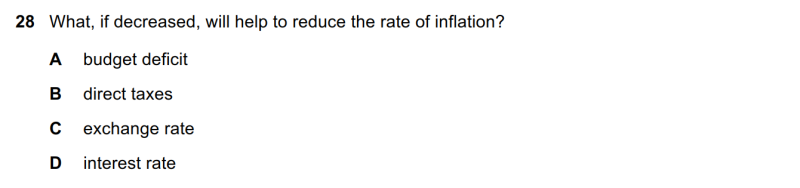“9708 s22 qp 12”的版本间的差异
跳到导航
跳到搜索
【点此返回历年真题目录】
(创建页面,内容为“<center><big>'''【点此返回历年真题目录】'''</big></center> <br/> <big>'''单题搜索方法''':右上角搜索中…”) |
|||
| 第38行: | 第38行: | ||
==题目解答== | ==题目解答== | ||
===1=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_1.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || positive和normative statement的概念和区分 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● positive statement是客观的,强调证据、验证、事实,因此D选项符合题意。<br/>● A、B、C三个选项中都涉及到了主观性的词语,如better、ought、subjective等,均排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>1 Which list has the most words that are more likely to relate to a positive statement than to a normative statement? A describe, better, should, value, emotion B bias, objective, ought, opinion, tastes C contestable, is, motive, subjective, moral D actual, ethics, fact, was, testable</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===2=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_2.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' B'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || planned economy的识别 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 计划经济完全由国家来进行物资的生产与分配,因此B选项正确。<br/>● A、D两个选项属于market economy的特征,C选项属于mixed economy的特征,均排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>2 What is the main characteristic of a planned economy? A All goods and services are produced by privately-owned firms. B All goods and services are produced by state-owned firms. C Privately-owned firms produce private goods and state-owned firms produce public goods. D The price mechanism allocates scarce resources through the actions of buyers and sellers.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===3=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_3.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || PPC线上点的含义 | |||
|- | |||
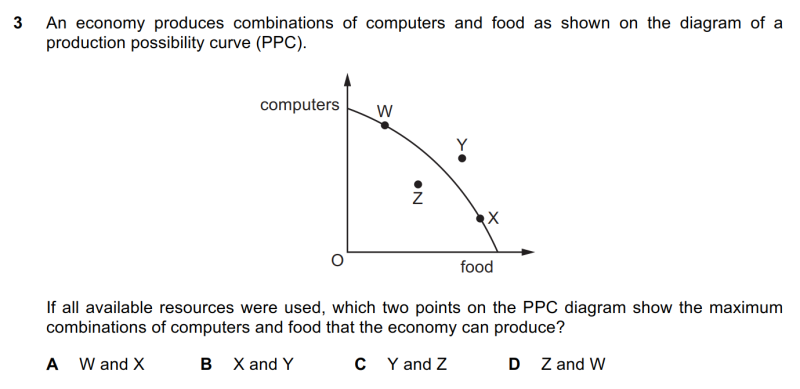
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 资源全部有效率用尽时,生产点应位于PPC线上,因此W和X满足题意,A选项正确。<br/>● Y点现阶段无法达到。Z点没有有效用尽资源。均排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>3 An economy produces combinations of computers and food as shown on the diagram of a production possibility curve (PPC). If all available resources were used, which two points on the PPC diagram show the maximum combinations of computers and food that the economy can produce? A W and X B X and Y C Y and Z D Z and W</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===4=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_4.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || money的职能 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 货币职能包括medium of exchange、unit of account、deferred payment和store of value。表中的三项全部属于货币职能,因此A选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>4 Four students have to complete a table showing the functions of money. Which student is correct?</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===5=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_5.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || PES的影响因素 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,讲的是demand方面,与PES关系不大。排除。<br/>● B选项,生产者很容易转到该行业,因此价格上涨一点,供给量就可以增加很多,PES偏大,排除。<br/>● C选项,需要高技能劳动力,因此价格上涨时,供给量很难迅速提高(难以找到适合的劳动力),符合题意,正确。<br/>● D选项,生产原材料充足,因此价格上涨时,供给量可以快速提升,PES偏大,排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>5 In which situation is the price elasticity of supply for a product most likely to be relatively low? A Demand for the product comes from a wide range of customers. B Producers in closely related industries can easily switch to making the product. C Manufacture of the product requires highly skilled labour. D The main raw material used in the production of the product is in abundant supply.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===6=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_6.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || consumer surplus的变化 | |||
|- | |||
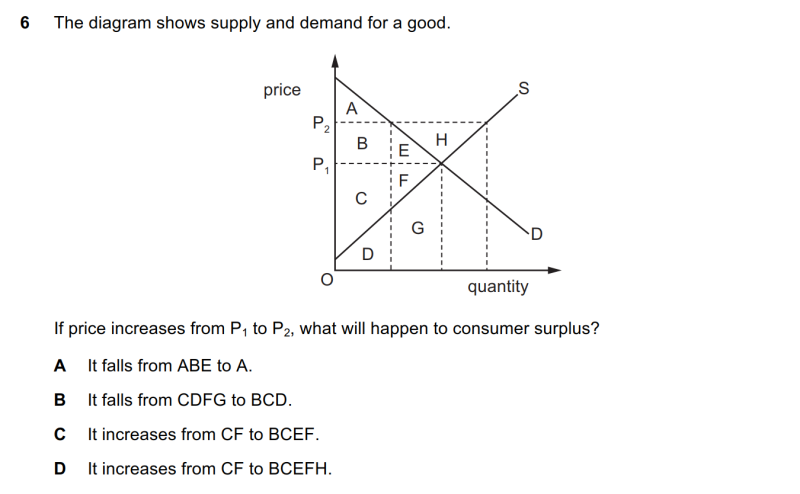
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● consumer surplus是D线、价格线与y轴围出的三角形。当价格为P<sub>1</sub>时,消费者剩余为ABE之和。当价格为P<sub>2</sub>时,消费者剩余为A。因此A选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>6 The diagram shows supply and demand for a good. If price increases from P1 to P2, what will happen to consumer surplus? A It falls from ABE to A. B It falls from CDFG to BCD. C It increases from CF to BCEF. D It increases from CF to BCEFH.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===7=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_7.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || D线与S线的作用 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● C选项,D线和S线是制定市场价格的重要影响因素,符合题意,正确。<br/>● A、B、D三个选项,自由市场并非最大化人们的福利,不是按需分配并注重平等,均排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>7 What can be concluded about the roles of demand and supply in a free market? A They allocate resources to the greatest needs. B They ensure that goods and services are distributed equally. C They are both significant in setting the market price. D They ensure that everyone can benefit from the good or service provided.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===8=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_8.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 影响D线的因素 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 成功的广告会提高人们对产品的需求,D线右移。因此C选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>8 A firm has a successful advertising campaign for a good. Which combination shows the impact on demand or supply and the associated reason? A a leftward shift in the good’s demand curve, as increased advertising cost raises the price of the product and reduces its demand B a rightward shift in the good’s supply curve, as the advertising cost of the firm increases C a rightward shift in the good’s demand curve, as successful advertising increases demand D a leftward shift in the good’s supply curve, as successful advertising enables firms to sell more</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===9=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_9.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' B'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || PED对企业的商业价值 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● PED对企业的商业价值主要体现在PED与TR的关系上,商品的PED不同,需要采取不同的定价策略才能达到提高TR和profit的目的。因此B选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>9 What would be the most likely reason for a firm’s decision to calculate the price elasticity of demand for its product? A to provide retail statistics for the government B to predict the change in its total revenue after it raises prices C to calculate the firm’s competitive position D to enable the firm to complete consumer satisfaction surveys</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===10=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_10.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || XED的作用 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● XED为正说明是替代品,为负说明是互补品。因此S与P是替代品,S与R是互补品,P与R是互补品。<br/>● 综上所述,C选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>10 The cross-elasticity of demand of good S with respect to the price of good P is +1.5. The cross-elasticity of demand of good S with respect to the price of good R is –1.5. The cross-elasticity of demand of good P with respect to the price of good R is –1.5. What can be concluded about goods P, R and S? A S and P are complements; P and R are substitutes. B S and P are complements; R is an inferior good. C S and P are substitutes; P and R are complements. D S and P are substitutes; R is an inferior good.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===11=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_11.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 影响D线的因素 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,收入下降导致D线左移,替代品价格上升导致D线右移。D线很可能不动,符合题意,正确。<br/>● B选项,收入下降导致D线左移,本产品价格上升导致点沿D线下降。D线位置已经变化。B选项错误。<br/>● C选项,收入上升导致D线右移,替代品价格上升导致D线右移。D线位置已经变化。C选项错误。<br/>● D选项,收入上升导致D线右移,本产品价格上升导致点沿D线下降。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>11 Which combination of events is most likely to leave the demand curve for a normal good in the same position? A a decrease in consumer incomes and an increase in the price of a substitute good B a decrease in consumer incomes and an increase in the price of the good C an increase in consumer incomes and an increase in the price of a substitute good D an increase in consumer incomes and an increase in the price of the good</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===12=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_12.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || price mechanism的表现 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,因为public goods市场上不提供,因此没有价格可言,价格没法起到分配资源的效果,正确。<br/>● B、C、D三个选项都能够体现出价格在市场中的作用(function),因此均不符合题意,排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>12 What does not happen when price acts as a means to allocate resources? A Price determines the supply of public goods. B Price operates in the markets for both goods and factors of production. C Price recognises consumers’ ability to pay rather than consumers’ needs. D Price signals to producers which goods are most profitable.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===13=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_13.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || market disequilibrium的表现 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,如果市场是自由的,那么不均衡时的价格最终会回归到均衡时的价格,所以价格会改变。<br/>● B选项,只有市场均衡时S才等于D,不均衡时是不等的。错误。<br/>● C选项,如果市场是自由的,可以由市场自己调节回去。错误。<br/>● D选项,市场不均衡可能会造成shortage短缺,也可能会造成surplus盈余。D选项错误。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>13 Which statement about market disequilibrium is correct? A Price is likely to change. B Supply is equal to demand. C The government must intervene. D There must be shortages.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===14=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_14.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || regressive tax的判定 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● regressive tax整体来说对低收入群体不利。<br/>● D选项,移除收入税的免税门槛和征收VAT都是对低收入群体不利的税收政策,可认为是regressive tax。<br/>● A选项中的提高财富税税率、B选项的引入财富税和提高收入税都属于progressive tax,对高收入群体不利,均排除。C选项的降低收入税的基础税率(最低一级的税率),对低收入群体有利。排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>14 Which combination of tax changes is most likely to be regressive in a developed economy? A increasing the rate of wealth tax and raising the rate of sales tax (VAT) on luxury products B introducing a tax on owning property based on its sales value and increasing the rate of income tax C reducing the basic rate of income tax and increasing the duty on fuel D removing the tax-free allowance for income tax and extending sales tax (VAT) to include all food</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===15=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_15.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|red|{{color|white|''' 困难 '''}}}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 市场均衡价格、price control、市场不均衡的类别 | |||
|- | |||
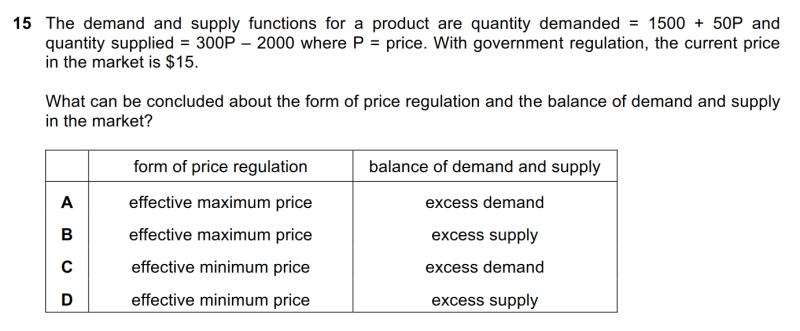
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 市场均衡时,D=S。根据市场的D线与S线的方程,可以算出均衡价格P=14。此时真实价格为15,高于均衡价格,因此属于有效的minimum price。市场上出现surplus,即excess supply。D选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>15 The demand and supply functions for a product are quantity demanded = 1500 + 50P and quantity supplied = 300P – 2000 where P = price. With government regulation, the current price in the market is $15. What can be concluded about the form of price regulation and the balance of demand and supply in the market? A effective maximum price excess demand B effective maximum price excess supply C effective minimum price excess demand D effective minimum price excess supply</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===16=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_16.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 补贴的作用、D线的影响因素 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 政府对电动汽车进行补贴,则电动汽车的产量会上升。这会带动人们对电力的需求,电的D线会右移,价格上升,数量增加。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>16 To improve the air quality for its citizens, a government introduces a subsidy for the producers of cars powered by batteries charged from the electricity supply. What are the likely effects of this subsidy on the price and sales of electricity? price of electricity sales of electricity A falls falls B falls rises C rises falls D rises rises</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===17=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_17.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || transfer payment的识别 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● transfer payment指的是与生产无关的各类收入,因此绝对不可能包括production,D选项符合要求,正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>17 What is definitely not involved when a transfer payment is made? A bank deposits B cash C government D production</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===18=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_18.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 政府提供public goods的影响 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,public goods的特征包括non-excludability,所以会提升,排除。<br/>● B选项,public goods的存在是市场失灵的原因之一,因此纠正后资源能够更有效利用。<br/>● C选项,政府提供public goods会花很多政府预算,这些钱将不能用于调节其他领域,因此存在机会成本。排除。<br/>● D选项,政府想多提供public goods,需要征更多的税收,因此减税不太可能发生,D选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>18 What is unlikely to occur with an increase in the provision of public goods? A consumer non-excludability B improved use of resources C opportunity cost D reduction in tax</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===19=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_19.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || AD的影响因素 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 消费下降了,但经济整体情况没有明显下降,说明其他因素上升了。A选项正确。其余选项均是导致AD下降的情况。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>19 In 2020, shops reported a fall in sales as domestic demand in an economy fell. However, the impact on the overall economy was not as unfavourable as was first feared. What might have lessened the impact on the economy? A Exports increased. B Imports increased. C Savings increased. D Taxes increased.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===20=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_20.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || trade-weighted exchange rate的意义 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● trade-weighted exchange rate计算的是本国货币针对多国货币汇率的平均变化情况,因此和trading partners有关,C选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>20 What does a trade-weighted exchange rate attempt to take account of? A a country’s terms of trade B international trade as a proportion of a country’s national income C the relative value of international trade done with a country’s trading partners D the size of a country’s current account surplus or deficit</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===21=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_21.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || terms of trade的概念 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● TOT要上升,需要使出口价格(分子)增长快于进口价格(分母)增长。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>21 What will lead to an improvement in the terms of trade? A Export prices fall by 10% and import prices fall by 5%. B Export prices fall by 10% and import prices rise by 5%. C Export prices rise by 5% and import prices rise by 10%. D Export prices rise by 10% and import prices rise by 5%.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===22=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_22.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 通胀/通缩与价格水平、货币购买力的关系 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,2013-2014年的通胀率大于0,所以价格水平是上升的,排除。<br/>● B选项,2014-2015年已经处于通缩状态,并非disinflation(其也是inflation中的一种情况),排除。<br/>● C选项,2014-2015年通缩,价格水平下降,货币的购买力上升。正确。<br/>● D选项,2016年后,经济再度通胀,生活成本下降。排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>22 The diagram shows the annual inflation rate in an economy. What can be deduced from the graph? A The price of goods and services fell between 2013 and 2014. B Disinflation took place between 2014 and 2015. C The purchasing power of money increased between 2014 and 2015. D The cost of living fell from 2016 onwards.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===23=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_23.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 固定汇率下贬值原因 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 国家企图下调汇率,说明此时市场均衡汇率已经严重低于固定汇率。<br/>● A选项,本国通胀低,说明出口价格低,出口增加,货币市场MD线右移,市场汇率上升,排除。<br/>● B选项针对本国的关税下降,出口增加,和A选项影响一致,排除。<br/>● C选项,current account逆差增加,说明出口下降或进口增加,这会导致MD左移或MS右移,无论哪种情况,市场汇率都会下降。正确。<br/>● D选项,本国利率高,货币进入本国逐利,货币市场MD右移,市场汇率上升,排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>23 A country operates a fixed exchange rate system. What will put pressure on the country to devalue its currency? A a decrease in the country’s inflation rate relative to the inflation rates of other countries B a decrease in the tariffs on its products imposed by other countries C an increase in its current account balance of payments deficit with other countries D an increase in the country’s interest rate relative to the interest rates of other countries</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===24=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_24.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || Marshall-Lerner condition的应用 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 贬值后,如果M-L条件成立,则current account deficit会下降(改善);如果条件不成立,则current account deficit则会恶化。<br/>● 按照题意,需要选择进出口PED之和低于1的选项,即A选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>24 The table gives different combinations of possible values for a country’s price elasticity of demand for exports and price elasticity of demand for its imports. Following the devaluation of the country’s currency, under which combination of elasticities would the country’s balance of payments on the current account worsen? A 0.3 0.3 B 0.2 0.9 C 0.6 0.5 D 1.2 1.2</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===25=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_25.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' B'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || tariff的影响 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 收关税后,商品价格上升,因此B选项正确。<br/>● A选项,由于价格上升,需求量会下降,排除。<br/>● C选项,收关税会增加政府税收。排除。<br/>● D选项,进口量为本国shortage的数量,随着价格提升,shortage逐渐减少,因此进口下降。排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>25 A small country imposes no tariffs and has a perfectly elastic supply of smartphones from the rest of the world. Which statement is correct after the imposition of a tariff? A The domestic demand for smartphones will rise. B The domestic price of smartphones will rise. C The government will lose tax revenue. D The supply of imports will increase.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===26=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_26.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' D'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 贸易保护政策的判断 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 根据题目描述,日本自动限制了本国出口,属于voluntary export restraint,D选项正确。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>26 In a recent year, Japanese car manufacturers agreed to limit exports of cars to the USA. Which form of protectionism is this? A an embargo B an export subsidy C a quota D voluntary export restraint</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===27=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_27.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' C'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 影响SRAS的因素 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● 世界油价提高,本国企业生产成本上升(生产需消耗能源),因此SRAS左移,C正确。<br/>● A选项,先是SRAS上升,才出现cost-push inflation,因果倒置。即使考虑人们消费石油时感受到了通胀,也应该是AD的右移,因此A选项排除。<br/>● B选项,与A选项理由相同,属于因果倒置或应按照AD方面去理解,排除。<br/>● D选项,政府减税,SRAS应右移。排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>27 The diagram shows a shift in a country’s short-run aggregate supply curve from SRAS1 to SRAS2. The country imports oil. Why might an increase in the world price of oil have caused this shift? A A rise in inflation is expected. B Consumers face a fall in their disposable income. C Domestic firms’ costs have increased. D The government reduces tax on oil and petroleum products.</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===28=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_28.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 降低inflation的方法 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,预算赤字下降,说明Government spending减少或tax上升,这均有利于AD下降,通胀降低。正确。<br/>● B选项,税收下降,消费和投资上升,AD上升,通胀增加,排除。<br/>● C选项,汇率下降(贬值)会导致出口增加、进口下降,因此AD上升,投资增加,排除。<br/>● D选项,利率下降,借贷成本下降,消费和投资上升,AD上升,通胀增加,排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>28 What, if decreased, will help to reduce the rate of inflation? A budget deficit B direct taxes C exchange rate D interest rate</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===29=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_29.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' B'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#00FF00|''' 容易 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || contractionary fiscal policy的识别 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● contractionary fiscal policy包括税收上升或政府支出下降,这会带来budget surplus的增加或budget deficit的下降,因此B选项正确,A选项错误。<br/>● C、D两个选项属于货币政策,与fiscal policy无关。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>29 What is an example of contractionary fiscal policy? A an increase in the budget deficit B an increase in the budget surplus C an increase in the interest rate D an increase in the money supply</small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
===30=== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''题目''' || || style="background: #FAF0E6"| [[File: 9708_s22_qp_12_30.png|800px]] | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''答案''' || || <big><big>''' A'''</big></big> | |||
|- | |||
| align="right"|'''难度''' || || {{Background color|#FFC20E|''' 中等 '''}} | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top"|'''考察知识点''' || || 宏观政策的有效性分析 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''解答要点''' || || ● A选项,贬值会提高出口、降低进口,因此经济增长,失业率下降,但造成demand-pull inflation。符合题意,正确。<br/>● B选项,高直接税会降低收入和利润,因此消费和投资下降,经济下降,失业增加,也会带来bad deflation。与题意不符,排除。<br/>● C选项,高关税会减少进口,经济增长,但增长的幅度可能不如A选项高(出口影响不确定,甚至可能会因为本国贸易保护而引发外国采取同样措施反制)。不如A选项合理。<br/>● D选项,高利率会引起借贷成本上升,消费和投资下降,经济下降,失业增加,也会带来bad deflation。与题意不符,排除。 | |||
|- | |||
| align="right" valign="top" width="100px" |'''文字版备查''' || || <small>30 A country with low unemployment and a managed floating exchange rate has a persistent current account deficit on its balance of payments. Which policy to reduce this deficit is most likely to keep unemployment low, but cause inflation? A depreciating its currency B higher direct taxation C higher import tariffs D higher interest rates </small> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
2022年8月17日 (三) 02:00的版本
单题搜索方法:右上角搜索中输入该题题干中的部分文字,点击搜索后进入相关页面,然后使用ctrl+F5(或其他按键组合调出搜索框),再次搜索该题干文字,直接定位到题目。
整卷下载
- 试卷请点击此处 ⇒ 【9708_s22_qp_12】
- 答案请点击此处 ⇒ 【9708_s22_ms_12】
试卷难易度分析
| 考察章节 | 容易 | 中等 | 困难 | 总计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chapter 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Chapter 2 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 11 |
| Chapter 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Chapter 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Chapter 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Chapter 6 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 7 |
| Chapter 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Chapter 11 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 总计 | 8 | 19 | 3 | 30 |
题目解答
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30