“9708 m23 qp 22”的版本间的差异
(创建页面,内容为“<center><big>'''【点此返回历年真题目录】'''</big></center> <br/> <big>'''单题搜索方法''':右上角搜索中…”) |
|||
| 第25行: | 第25行: | ||
!原文!!参考译文(谷歌机翻) | !原文!!参考译文(谷歌机翻) | ||
|-valign="top" | |-valign="top" | ||
|''' | |'''Inflation in the United States (US)'''<br/><br/> | ||
Prices are rising much faster than expected across the world's economies, including the US. As the US economy has grown, the prices of goods and services have substantially increased. The US economy is forecast to grow by 7.4% in 2021, with consumer spending rising by over 10% per year, but this boom has been accompanied by a rapid increase in the inflation rate. <br/> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
The US inflation rate was 1.7% in February 2021. By the end of that year it had been expected to be 1.9%, but by June 2021 the rate was already 5.4% compared with 12 months before. This is the highest rate of inflation in the US since August 2008. <br/> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
Rising | Rising inflation in the US has two main causes. The first cause is a substantial increase in the demand for consumer spending on goods and services. The economy has also been boosted by the US government’s economic stimulus package in response to the downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2020 and 2021, the US government spent an additional US$6 trillion, leading to a budget deficit of 12.7% of gross domestic product (GDP) in June 2021, one of the largest budget deficits in the world. <br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
The second cause of increasing inflation in the US is significant disruption to the supply of many goods as a result of the pandemic, a problem worsened by disruption to global shipping created by the temporary blocking of the Suez Canal. There are now long-term supply shortages for a wide range of products from semiconductors to timber. The cost of shipping goods has also become more expensive; for example, the cost of shipping goods from China to the US has tripled over 12 months. <br/> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
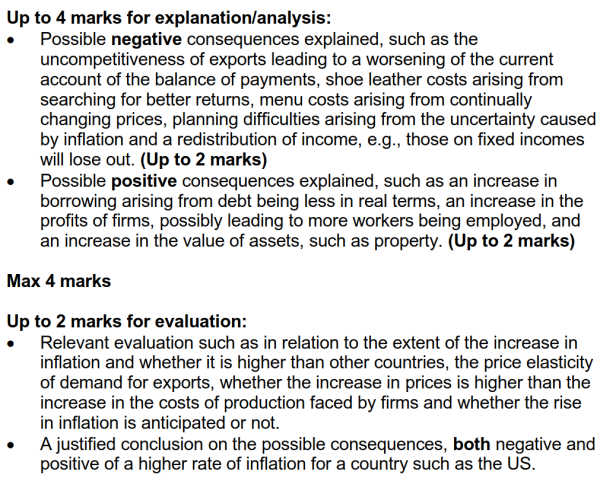
A sustained increase in inflation could have a number of consequences, both negative and positive. Rising inflation could lead to a tightening of monetary policy, such as through an increase in interest rates. This is important in the US given that the government is targeting an annual inflation rate of 2%. Some economists believe that interest rates in the US may need to rise from 0.25% to as high as 4.50% to ‘cool’ the economy and reduce the rate of inflation and that this is likely to happen sooner rather than later. | |||
||''' | ||'''美国的通货膨胀'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
包括美国在内的全球经济体的价格上涨速度远超预期。随着美国经济的增长,商品和服务的价格大幅上涨。预计2021年美国经济将增长7.4%,消费者支出每年增长10%以上,但这种繁荣伴随着通货膨胀率的快速上升。<br> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
2021年2月,美国通货膨胀率为1.7%。到当年年底,预计为1.9%,但到2021年6月,与12个月前相比,该通胀率已经达到5.4%。这是美国自2008年8月以来的最高通货膨胀率。<br> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
美国通胀上升有两个主要原因。第一个原因是消费者对商品和服务支出的需求大幅增加。美国政府为应对COVID-19大流行造成的经济低迷而推出的经济刺激计划也提振了经济。2020年和2021年,美国政府额外支出6万亿美元,导致2021年6月的预算赤字占国内生产总值(GDP)的12.7%,是世界上最大的预算赤字之一。<br> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
美国通货膨胀加剧的第二个原因是大流行导致许多商品供应严重中断,苏伊士运河暂时封锁造成的全球航运中断使这一问题更加严重。现在,从半导体到木材,范围广泛的产品都存在长期供应短缺的问题。运输货物的成本也变得更加昂贵;例如,从中国运往美国的货物成本在12个月内增加了两倍。<br> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
通货膨胀的持续增加可能会产生许多负面和正面的后果。通胀上升可能导致货币政策收紧,例如通过提高利率。这在美国很重要,因为政府的目标是年通胀率为2%。一些经济学家认为,美国的利率可能需要从0.25%上升到高达4.50%才能“冷却”经济并降低通货膨胀率,而且这可能会早不宜迟。 | |||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
2023年6月10日 (六) 01:41的版本
单题搜索方法:右上角搜索中输入该题中的部分文字,点击搜索后进入相关页面,然后使用ctrl+F5(或其他按键组合调出搜索框),再次搜索该题干文字,直接定位到题目。
整卷下载
- 试卷请点击此处 ⇒ 【9708_m23_qp_22】
- 答案请点击此处 ⇒ 【9708_m23_ms_22】
关于难度分类的说明:
容易 :概念类、识别类、公式计算类
中等 :原因分析类、影响分析类、图像分析类、计算分析类
困难 :全新概念类、全新场景类、全新图像类、推导复杂类、观点评价类、对比评价类、政策评价类
Data response

中英对照
| 原文 | 参考译文(谷歌机翻) |
|---|---|
| Inflation in the United States (US) Prices are rising much faster than expected across the world's economies, including the US. As the US economy has grown, the prices of goods and services have substantially increased. The US economy is forecast to grow by 7.4% in 2021, with consumer spending rising by over 10% per year, but this boom has been accompanied by a rapid increase in the inflation rate. |
美国的通货膨胀
|