Edexcel IAL U2 revision - Section 1 (2018)
如遇到公式加载异常,请刷新页面!
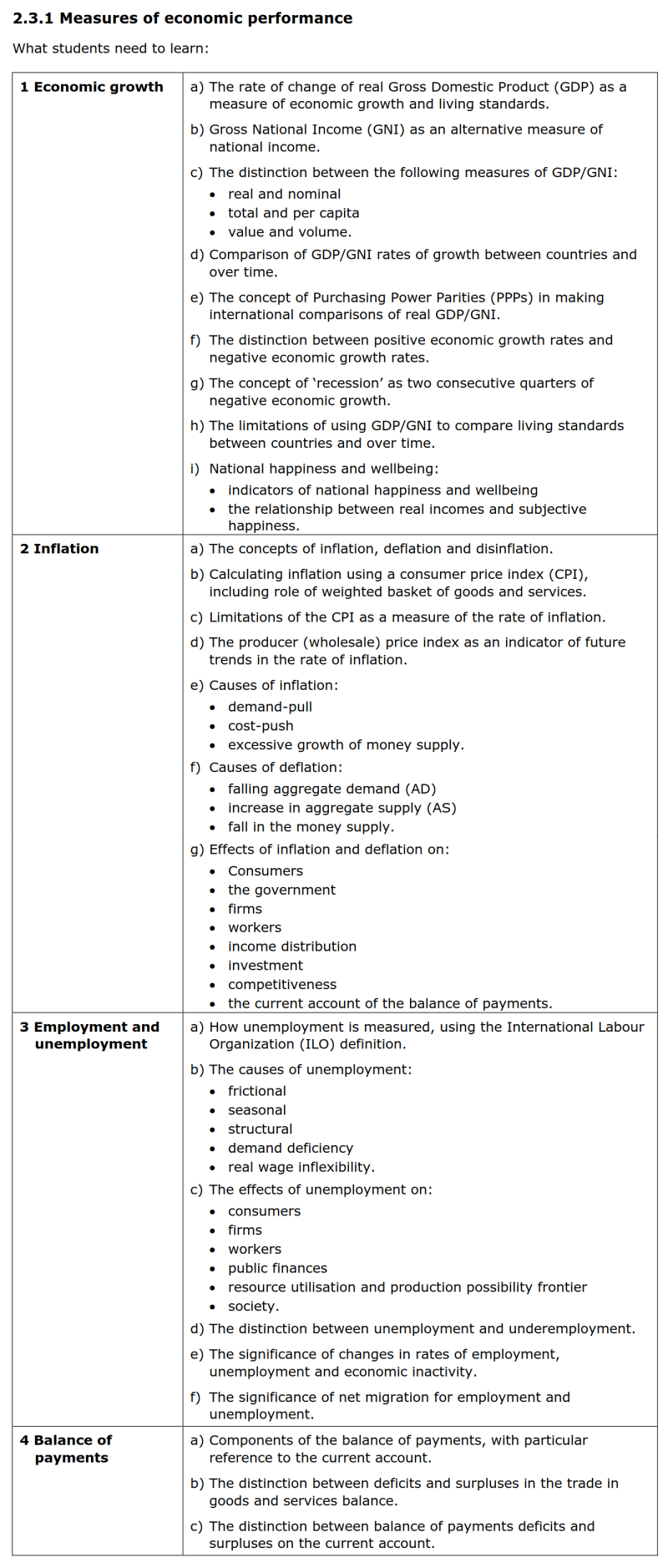
Section 1 Measures of economic performance 经济表现的测量
- 大纲要求
1. Economic growth 经济增长
a) The rate of change of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as a measure of economic growth and living standards. 使用实际国内生产总值(GDP)变化率作为经济增长和生活水平的衡量指标
b) Gross National Income (GNI) as an alternative measure of national income. 使用总国民收入(GNI)作为国民收入的替代衡量指标
c) The distinction between the following measures of GDP/GNI: 下列GDP与GNI之间的区别:
• real and nominal 实际值与名义值
• total and per capita 总值与人均值
• value and volume. 价值与数量
d) Comparison of GDP/GNI rates of growth between countries and over time. 按照国别和时间进行GDP或GNI增长率的比较
e) The concept of Purchasing Power Parities (PPPs) in making international comparisons of real GDP/GNI. 在国际比较实际GDP或实际GNI时,购买力平价的概念
f) The distinction between positive economic growth rates and negative economic growth rates. 正经济增长率与负经济增长率之间的区别
g) The concept of ‘recession’ as two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth. 衰退指的是两个连续季度出现负经济增长
h) The limitations of using GDP/GNI to compare living standards between countries and over time. 使用GDP或GNI去比较国家间和不同时间段的生活质量的局限性
i) National happiness and wellbeing: 国民幸福度与福利
• indicators of national happiness and wellbeing 用于衡量国民幸福度与福利的指标
• the relationship between real incomes and subjective happiness. 实际收入与主观幸福度之间的关系
2. Inflation 通货膨胀
a) The concepts of inflation, deflation and disinflation. 通货膨胀、通货紧缩、反通货膨胀的概念
b) Calculating inflation using a consumer price index (CPI), including role of weighted basket of goods and services. 使用消费者价格指数CPI计算通胀水平,其包含一系列带权重的商品和服务
c) Limitations of the CPI as a measure of the rate of inflation. CPI作为通胀率估计的局限性
d) The producer (wholesale) price index as an indicator of future trends in the rate of inflation. 生产者价格指数作为通胀率未来趋势的估计指标
e) Causes of inflation: 通胀的原因
• demand-pull 需求拉动型通胀
• cost-push 成本推动型通胀
• excessive growth of money supply. 货币供给的超额增长
f) Causes of deflation: 通缩的原因
• falling aggregate demand (AD) 总需求的下降
• increase in aggregate supply (AS) 总供给的上升
• fall in the money supply. 货币供给的下降
g) Effects of inflation and deflation on: 通胀与通缩对以下方面的影响:
• Consumers 消费者
• the government 政府
• firms 企业
• workers 工人
• income distribution 收入分配
• investment 投资
• competitiveness 竞争
• the current account of the balance of payments. 国际收支账户的经常账户
3. Employment and unemployment 就业与失业
a) How unemployment is measured, using the International Labour Organization (ILO) definition. 按照国际劳工组织的定义,失业是如何测量的
b) The causes of unemployment: 失业的原因
• frictional 摩擦型失业
• seasonal 季节型失业
• structural 结构型失业
• demand deficiency 需求不足型失业(周期型失业)
• real wage inflexibility. 实际工资缺乏灵活型失业
c) The effects of unemployment on: 失业对以下情形的影响:
• consumers 消费者
• firms 企业
• workers 工人
• public finances 公共部门财政资金
• resource utilisation and production possibility frontier 资源利用与生产可能性曲线
• society. 社会
d) The distinction between unemployment and underemployment. 失业与未充分就业之间的区别
e) The significance of changes in rates of employment, unemployment and economic inactivity. 就业率、失业率和经济不活跃人口率变化的重要性
f) The significance of net migration for employment and unemployment. 净移民对就业与失业的重要性
4. Balance of payments 国际收支账户
a) Components of the balance of payments, with particular reference to the current account. 国际收支账户的组成部分,包括经常账户的组成
b) The distinction between deficits and surpluses in the trade in goods and services balance. 商品和服务贸易的顺差和逆差之间的区别
c) The distinction between balance of payments deficits and surpluses on the current account. 经常账户的顺差和逆差之间的区别