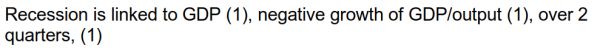【点此返回历年真题目录】
单题搜索方法:右上角搜索中输入该题中的部分文字,点击搜索后进入相关页面,然后使用ctrl+F5(或其他按键组合调出搜索框),再次搜索该题干文字,直接定位到题目。
整卷下载
关于难度分类的说明:
容易 :概念类、识别类、公式计算类
中等 :原因分析类、影响分析类、图像分析类、计算分析类
困难 :全新概念类、全新场景类、全新图像类、推导复杂类、观点评价类、对比评价类、政策评价类
Data response

中英对照
| 原文 |
参考译文(谷歌机翻)
|
Vietnam's ‘Economic Miracle’
Thirty years ago, Vietnam was one of the poorest countries in Southeast Asia. Since then, its real GDP has increased rapidly. A series of economic and political reforms has been responsible for its so-called ‘economic miracle’.
Vietnam has benefitted from the increased protectionism in trade between China and the United States (US). For example, Vietnam has increased production of goods that are substitutes to those made in China to such an extent that Vietnam is popularly referred to as ‘China plus one’, in recognition of its similar comparative advantage to China.
Rising export revenue is only one reason for Vietnam’s spectacular economic growth. With a rapidly growing population, Vietnam has invested heavily in its human capital and physical capital in the form of infrastructure, including cheap access to the internet.
A third reason for this success is how Vietnam has moved towards trade liberalisation. This is shown through its free trade agreement with the US and its membership of organisations of countries that have agreed to trade freely with each other, such as ASEAN and the TPP. These initiatives involve the removal of tariffs and other tools of protection, increasing the potential for Vietnam to trade with other countries.
Nevertheless, there are possible dangers in this strategy. Vietnam’s economy is heavily dependent on its exports which in 2017 were over 90% of GDP. This reliance puts Vietnam at risk from downturns in the global economy and in the economies of its main trading partners. Even more worrying is the repeated threat from the US that it may put import tariffs on manufactured goods from Vietnam.
|
越南的“经济奇迹”
三十年前,越南是东南亚最贫穷的国家之一。此后,其实际GDP迅速增长。一系列经济和政治改革为其所谓的“经济奇迹”负责。
越南受益于中美贸易保护主义的加剧。例如,越南增加了替代中国制造的商品的生产,以至于越南被普遍称为“中国加一”,以承认其与中国相似的比较优势。
出口收入的增加只是越南经济高速增长的原因之一。随着人口的快速增长,越南以基础设施的形式大力投资于人力资本和物质资本,包括廉价的互联网接入。
这一成功的第三个原因是越南如何走向贸易自由化。这体现在它与美国的自由贸易协定以及它在东盟和 TPP 等已同意相互自由贸易的国家组织中的成员身份。这些举措包括取消关税和其他保护工具,增加越南与其他国家贸易的潜力。
然而,这种策略可能存在危险。越南经济严重依赖出口,2017 年出口占 GDP 的比重超过 90%。这种依赖使越南面临全球经济及其主要贸易伙伴经济下滑的风险。更令人担忧的是,美国一再威胁要对越南制成品征收进口关税。
|
| 题目1a |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
概念识别
|
| 难度 |
|
容易
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
recession的概念
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 写出recession的概念,注意强调GDP连续两个季度以上负增长。
|
| 官方答案 |
|
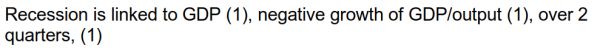
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(a) State what is meant by ‘a recession’. [3]
|
| 题目1b |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析
|
| 难度 |
|
中等
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
government borrowing的原因;expansionary fiscal policy的作用
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 本题由两个问题组成,需要依次进行解答。
● 政府借贷的原因主要是为了补充财政赤字,如果支出大于税收收入,则需要借贷。
● 政府借贷后能够为政府支出提供更多资金,从而促进经济增长,增加就业,提高人们的收入和生活质量等。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(b) Analyse why governments borrow and why it is said that a government should increase spending in a recession. [5]
|
| 题目1c |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
crowding out的含义和影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 先写crowding out的定义,即政府支出会导致资源从私企流向国企(私企被排挤出市场)。
● 然后讨论产生这种情况的逻辑链。政府借贷会导致对货币需求上升,利率上升,私企借贷困难,投资减少。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(c) Consider what is meant by the phrase ‘government borrowing could ‘crowd out’ the private sector.’ [6]
|
| 题目1d |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
观点讨论
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
government borrowing的影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 本题需要分成借贷有好处和有问题两个角度进行分析。
● 好处包括没有crowding out、减少budget deficit。
● 问题包括债务水平为近60年最高、提高利率减少投资等。
● 最后给出结论,文中证据没有太多说服力inconclusive。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
(d) Assess whether the evidence in the article makes a conclusive case that the high level of government borrowing is an effective policy. [6]
|
| 题目2 |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析(含画图)
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
market failure;政府纠正市场失灵的方式
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 先写market failure、negative externality的定义,画出图像(负生产外部性和负消费外部性都要画一下),分析效率和deadweight loss,说明市场失灵带来的影响,比如over-consumption等。
● 然后考虑各类政府干预政策,比如税收、宣传、法律法规等。至少考虑2个政策,有些可以画图的政策(如税收)需要运用图像来说明。每个政策需要说明如何减少了市场失灵。
● 最后考虑evaluation,指出每个政策的问题,比如税收难以确定准确数量、宣传没有强制性、政府额外支出等。需要点评一下这些政策是否有必要进行,或者指出哪个政策最适合使用(比较各类政策的有用性)。
● 注意写总结段。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
2 The use of air travel leads to market failure caused by negative externalities. With the help of a diagram, assess the extent to which a government can intervene to correct this market failure. [20]
|
| 题目3 |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
观点讨论
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
oligopoly的特征;collusion的方式与影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
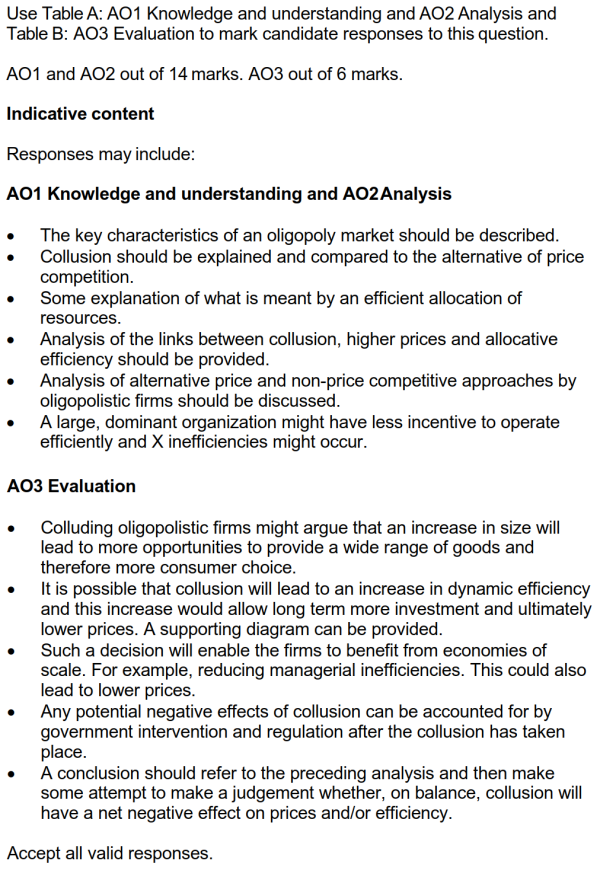
● 先说明oligopoly的assumptions(特征)。
● 解释寡头市场中的collusion,可适当使用game theory说明,指出cartel和price leadership并做适当解释。
● 对生产效率和分配效率进行解释,讨论在cartel和price leadership下,价格为何上升,效率为何下降。
● 讨论寡头市场中的竞争情况,说明一些竞争形式,如广告、售后服务、价格战等,解释这些竞争形式对价格和效率的影响,并与collusion对比,说明有些企业为何不选择竞争而选择合作。
● 最后考虑evaluation,说明寡头市场中的collusion有时也能带来一定的好处,比如技术进步和dynamic efficiency、产品选择性增加、企业扩张并享受economies of scale。此外,一些问题能够在政府干预下解决,可列举一些政府干预方式并说明如何减少寡头collusion带来的问题。
● 最后进行总结。
|
| 官方答案 |
|
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
3 Some firms in oligopoly markets choose to collude rather than engage in price competition. This will lead to higher prices and a less efficient allocation of resources. Evaluate this statement. [20]
|
| 题目4 |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
观点讨论
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
expenditure-reducing policy的具体形式及影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
● 先说明expenditure-reducing policies的定义。
● 解释具体的政策(至少2个),比如增加税收、减少政府支出、增加利率等,说明其如何降低AD,并解释其与减少current account deficit之间的关系。
● 再解释这些政策如何带来了更多的失业。失业需要进行类型的分析,指出cyclical unemployment会增加。
● 最后进行evaluation,比如如果还有supply-side policy则失业可能不会增加太多、部分失业类型和上述政策关系不大(比如frictional失业)、和经济所在阶段有关(经济过热时可以顺便纠正该状态)等。
● 注意结尾有总结段。
|
| 官方答案 |
|

|
| 文字版备查 |
|
4 Expenditure-reducing policies will reduce a balance of payments deficit but will also cause significant unemployment. Evaluate this statement. [20]
|
| 题目5 |
|

|
| 题目类型 |
|
文字分析
|
| 难度 |
|
困难
|
| 考察知识点 |
|
globalisation的影响
|
| 解答要点 |
|
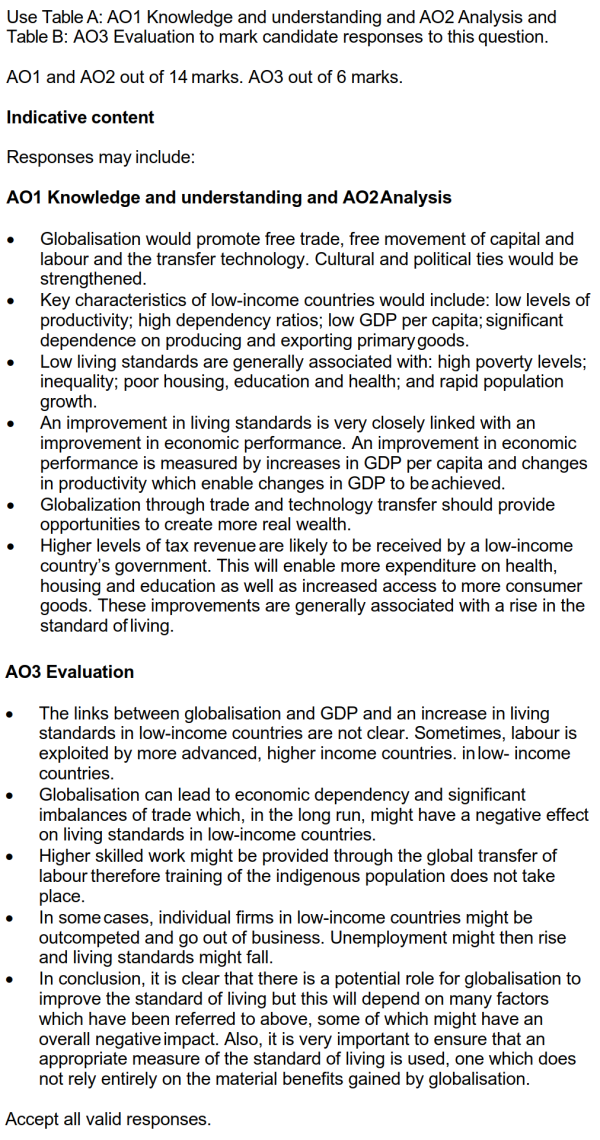
● 先说明globalisation的概念和特征、living standard包含的内容以及low-income countries的特征。
● 说明全球化如何改善了低收入国家的生活质量,比如增加产品种类、提升出口促进经济增长、技术和管理经验的引入、高关税收入以带来更多政府支出(改善教育、基建等)等。
● 最后进行evaluation,考虑全球化对低收入国家造成的不良影响,比如剥削工人、环境污染、terms of trade恶化、利润回流本国、突然撤资等。可考虑讨论全球化带来的好处多还是问题多。
● 注意结尾有总结段。
|
| 官方答案 |
|
|
| 文字版备查 |
|
5 Assess the impact of globalisation on the standard of living in low-income countries. [20]
|