CAIE IGCSE CS revision - Unit 5 (2023)
如遇到公式加载异常,请刷新页面!
Unit 5 The internet and its uses 互联网及其用途
5.1 The internet and the world wide web 互联网和万维网
- 大纲要求
5.1.1 Understand the difference between the internet and the world wide web 理解因特网和万维网的区别
• The internet is the infrastructure 互联网是基础设施
• The world wide web is the collection of websites and web pages accessed using the internet 万维网是使用互联网访问的网站和网页的集合
- Internet:因特网,指世界范围内网络的相互连接。
- 注意:Internet因特网使用TCP/IP协议。
- World Wide Web(WWW):由hypertext transfer protocols(http或https)超文本传输协议连接起来的网站与网页的集合。
5.1.2 Understand what is meant by a uniform resource locator (URL) 理解统一资源定位器(URL)的含义
• A URL is a text-based address for a web page; it can contain the protocol, the domain name and the web page/file name URL是基于文本的网页地址。它可以包含协议、域名和网页/文件名
- uniform resource locator(URL):统一资源定位器,指网站使用的文本书写形式的地址。
- URL的基本形式:protocol://website address/path/file name
- Protocol:协议,一般是http或https。
- Website address:网页地址,包含以下部分:
- Domain host:域主机,一般是www。
- Domain name:域名,指网站的文本地址名,不同的网站有不同的域名。
- Domain type:域类型,比如.com、.net、.gov等。
- Country code:国家代码,有些网站有该部分,比如.uk、.de、.cn等。
- Path:路径,即网页,有些时候可以忽略,即进入该网站的根目录。
- File name:文件名,即网页中的内容。
- URL的基本形式:protocol://website address/path/file name
5.1.3 Describe the purpose and operation of hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) and hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) 描述超文本传输协议(HTTP)和安全超文本传输协议(HTTPS)的目的和操作
- hypertext transfer protocol(HTTP):超文本传输协议,指在互联网中传递数据与文件所必须遵守的一系列rules规则。
- hypertext transfer protocol secure(HTTPS):超文本传输安全协议,指使用了某些安全加密措施(如SSL或TLS等)的HTTP。
5.1.4 Explain the purpose and functions of a web browser 解释网络浏览器的用途和功能
• The main purpose of a web browser is to render hypertext markup language (HTML) and display web pages Web 浏览器的主要目的是呈现超文本标记语言 (HTML) 和显示网页
• Functions include: 功能包括:
- storing bookmarks and favourites存储书签和收藏夹
- recording user history 记录用户历史记录
- allowing use of multiple tabs允许使用多个选项卡
- storing cookies存储cookie
- providing navigation tools提供导航工具
- providing an address bar提供地址栏
- Hypertext mark-up language(HTML):超文本标记语言,指用于设计、展示和格式化网页并编写http协议的语言。使用该语言编写的网页通过浏览器进行解读并显示。
- Browser:浏览器,用于连接域名服务器(DNS)以获取网站IP地址,并翻译网页的HTML,使得用户能够浏览网站上的文件和视频。
- 浏览器的功能:
- storing bookmarks and favourites:存储书签和收藏夹。用户可以保存自己需要的网页,以便之后快速访问
- recording user history:记录用户历史记录。便于用户追溯自己的浏览记录。
- allowing use of multiple tabs:允许使用多个选项卡。便于用户打开多个网页。
- storing cookies:存储cookie。便于用户储存自己的密码、喜好等,下次可以自动填充。【参考5.1.6】
- providing navigation tools:提供导航工具。便于用户快速访问一些网站。
- providing an address bar:提供地址栏。便于用户输入网站域名进行访问。
- 浏览器的功能:
5.1.5 Describe how web pages are located, retrieved and displayed on a device when a user enters a URL 描述当用户输入 URL 时网页如何定位、检索和显示在设备上
• Including the role of: 包括以下角色:
- the web browser网络浏览器
- IP addresses IP 地址
- domain name server (DNS) 域名服务器
- web server网络服务器
- HTML
- Domain name server(DNS):域名服务器,指通过网站的domain name域名查找相应的IP地址,以便计算机能够通过该IP地址连接上对方的网站服务器。
- 注意:DNS拥有着包含着URL和IP地址一一对应关系的数据库。
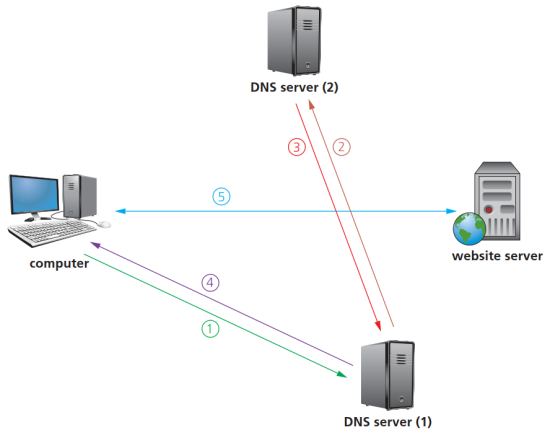
- 通过DNS查找网络服务器的步骤:
- 用户输入域名,计算机向DNS发送解读IP地址的请求。
- DNS开始搜索数据库。如果未搜索到,则将请求转发给下一台DNS服务器,直到搜索到对应记录。(一般会设置一个时限,如果在时限内未搜索到则显示超时)
- 搜索到的IP地址被回传给计算机(回传途中,原先未检索到该记录的DNS会将其计入数据库)。
- 计算机获得IP地址,按照该地址连接上对方网站服务器,下载相关页面的HTML,使用浏览器对其进行翻译,用户可以看到网页上的内容。
- 具体步骤示意图如下所示:
5.1.6 Explain what is meant by cookies and how they are used, including session cookies and persistent cookies 解释cookie的含义及其使用方法,包括会话cookie和持久cookie
• Cookies are used for functions, including: Cookie 用于以下功能,包括:
- saving personal details保存个人详细信息
- tracking user preferences追踪用户偏好
- holding items in an online shopping cart将商品保存在在线购物车中
- storing login details存储登录详细信息
- Cookies:指某些网站为了辨别用户身份而储存在用户本地终端上的数据,通常记录着用户的各类偏好。
- Cookies的分类:
- Session cookies:会话cookies,指暂时存放于计算机上,当浏览器关闭或会话结束后就自动删除的cookies。
- Cookies的分类:
- 注意:这些cookies不会收集用户的信息。
- 常见例子:某些网站的购物车。
- Persistent cookies:持久cookies,指存储在用户硬盘内,只有当用户自行删除或到了过期时间才会被删除的cookies。
- 常见用途:
- Allow the website to remember users’ passwords, email addresses and invoice details. 允许网站记住用户的密码、电子邮件地址等信息。
- Serve as a memory. 作为记录。
- Save users’ items in a virtual shopping basket/cart. 将用户的物品保存在虚拟购物篮/购物车中。
- Track internet habits and users’ website histories or favourites/bookmarks. 追踪互联网习惯和用户的网站历史记录或收藏夹/书签。
- Target users with advertising that matches their previous buying or surfing habits. 向用户投放符合他们之前购买或浏览习惯的广告。
- Store users’ preferences. 存储用户的偏好。
- Used in online financial transactions. 用于在线金融交易。
- Allow progress in online games and quizzes to be stored. 允许存储在线游戏和测验的进度。
- Allow social networking sites to recognise certain preferences and browsing histories. 允许社交网站识别某些偏好和浏览历史。
- Allow different languages to be used on the web pages automatically as soon as users log on. 允许用户登录后立即在网页上自动使用不同的语言。
- 常见用途:
- Persistent cookies:持久cookies,指存储在用户硬盘内,只有当用户自行删除或到了过期时间才会被删除的cookies。
5.2 Digital currency 数字货币
- 大纲要求
5.2.1 Understand the concept of a digital currency and how digital currencies are used 理解数字货币的概念以及数字货币的使用方式
• A digital currency is one that only exists electronically 数字货币是一种仅以电子方式存在的货币
- Digital currency:数字货币,指仅以electronic form电子形式存在的货币。
- 注意:数字货币属于数据库中的数据,没有物理形态。
- 注意:传统的电子货币由央行或政府管控。
- Cryptocurrency:加密货币,指使用decentralised去中心化技术来管控交易的数字货币。
- 注意:所谓的“去中心化”,指脱离央行或政府管控,全部规则和监管均由cryptocurrency community加密货币社区自行完成。
- 加密货币使用blockchain network区域链网络技术实现,安全性高。【参考5.2.2】
5.2.2 Understand the process of blockchain and how it is used to track digital currency transactions 了解区块链的过程以及如何使用它来跟踪数字货币交易
• Blockchain, in its basic form, is a digital ledger, that is a time-stamped series of records that cannot be altered 区块链的基本形式是一种数字分类账,即一系列带有时间戳且无法更改的记录
- Blockchain:区域链,指一个decentralised database去中心化的数据库,所有交易都存储在区块链网络中的所有计算机上;网络中有许多相互关联的计算机,但没有中央服务器。
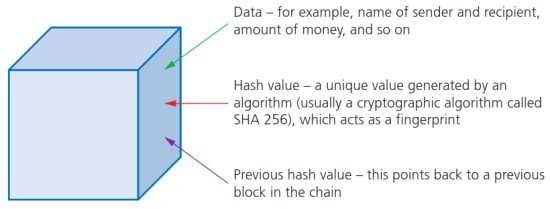
- Block区块的构成:
- Data:数据。可能是名字、货币金额等。
- Hash value:哈希值,是由加密算法(通常是SHA 256)计算出的唯一值。
- Previous hash value:前一个哈希值,用于指向区域链中的前一个块节点。
- Block区块的构成:
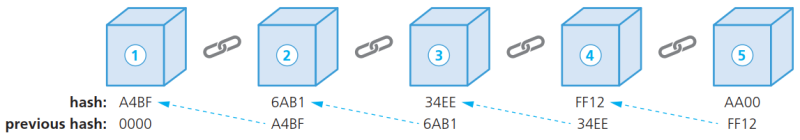
- Blockchain区域链的连接:
- Block ‘1’ 被称为genesis block创世区块。(前一位哈希值为0)
- 从block ‘2’ 开始,使用区块内的previous hash value前一个哈希值和前一区块构成连接。
- 任何区块内data数据的变化都会导致本区块的hash value哈希值发生改变,因此该区块之后的区块无法凭借previous hash value前一个哈希值与本区块构成连接,此时后续区块均变为invalid无效。该机制能够有效防止数据tampering篡改。
- 区域链构成如下图所示:
- Blockchain区域链的连接:
- Proof-of-work:工作证明,指区块链网络中用于确认交易,生成新区块以添加到链中的算法。称为miners矿工的特殊用户完成并监控网络上的交易以获得奖励。
- 通过一系列反向计算得出正确解的矿工们为了证明自己的工作量,需要提供工作证明,以此换取自己的区块报酬。
- Proof-of-work:工作证明,指区块链网络中用于确认交易,生成新区块以添加到链中的算法。称为miners矿工的特殊用户完成并监控网络上的交易以获得奖励。
5.3 Cybersecurity 网络安全
- 大纲要求
5.3.1 Describe the processes involved in, and the aim of carrying out, a range of cyber security threats 描述一系列网络安全威胁所涉及的过程和实施的目的
• Including: 包括:
- brute-force attack暴力攻击
- data interception数据拦截
- distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack分布式拒绝服务 (DDoS) 攻击
- hacking黑客攻击
- malware (virus, worm, Trojan horse, spyware, adware, ransomware) 恶意软件(病毒、蠕虫、特洛伊木马、间谍软件、广告软件、勒索软件)
- pharming网域嫁接
- phishing网络钓鱼
- social engineering 社交工程
- cyber security threats:网络安全威胁,指对网络安全存在不利影响的行为。
- brute-force attack:暴力攻击,指网络罪犯们通过穷举所有可能的密码组合,不断试错直到找到正确密码的行为。
- data interception:数据拦截,指通过eavesdrop监听有线或无线网络来非法获得数据。
- 常见的数据拦截手段:
- packet sniffing:数据包嗅探,网络罪犯们通过技术手段检查经由网络发送的数据包并查找数据包的内容,然后将这些内容发送给自己。
- wardriving:也称作access point mapping接入点映射,指使用笔记本电脑、天线、GPS设备和软件等拦截Wi-Fi信号并非法获取数据。
- 解决方法:
- Wired equivalency privacy (WEP) encryption protocol security有线等效保密 (WEP) 加密协议安全性
- Complex passwords for routers为路由器设置复杂密码
- Not use Wi-Fi (wireless) connectivity in public places不使用公共场所的Wi-Fi连接
- 常见的数据拦截手段:
- distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack:分布式拒绝服务 (DDoS) 攻击
- 常见的攻击手段:
- Denial of service (DoS) attack:拒绝服务攻击。网络罪犯们试图通过向网站发送大量请求来破坏网站的正常运行;或通过发送大量垃圾邮件来阻塞用户的邮箱。
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack:分布式拒绝服务 (DDoS) 攻击。DoS攻击中大量请求来自于不同的计算机,因此更难防范。
- 解决方法:
- Using an up-to-date malware checker. 使用最新的恶意软件检查程序
- Setting up a firewall to restrict traffic to and from the web server or user’s computer. 设置防火墙
- Applying email filters to filter out unwanted traffic. 应用电子邮件过滤器来过滤掉不需要的邮件
- 常见的攻击手段:
- Hacking:黑客攻击,指非法入侵计算机系统,可能会盗取或修改关键文件。
- 解决方法:
- The use of firewalls. 使用防火墙
- User names and frequently changed strong passwords. 妥善保存好用户名和密码,密码要设置为强密码且经常修改
- Anti-hacking software. 安装反黑客软件
- Ethical hacking:道德黑客行为(俗称“白帽黑客”),指被公司雇佣来排查安全系统并测试计算机系统面对黑客攻击时的安全情况的人员。
- 解决方法:
- Malware:恶意软件,指安装在用户计算机上的恶意程序(如virus病毒、worms蠕虫和Trojan houses特洛伊木马等),目的是非法删除、破坏或操纵数据。
- 常见的恶意软件:
- Virus:病毒,指可以replicate自我复制的程序或程序代码,目的是删除、破坏文件或导致计算机系统故障。病毒的激活需要依靠目标计算机上的活跃主程序。
- Worms:蠕虫,指一种可以自我复制的独立型恶意软件。蠕虫不需要活跃主程序,用户终端无需采取任何操作就可以在整个网络中传播。
- Trojan horse:特洛伊木马,指伪装成合法软件但其中包含可对计算机系统造成损害的恶意代码的恶意软件。特洛伊木马需要由用户运行才能起效。
- Spyware:间谍软件。该手段通过监视用户在计算机上的活动来收集信息,并将收集到的信息发送回发送间谍软件的网络罪犯。
- Adware:广告软件,指试图向用户发送不需要的广告的恶意软件。该手段本身非常小,但这意味着计算机系统安全性遭受破坏,很容易遭受其他恶意攻击,因此也需要引起重视。
- Ransomware:勒索软件,指对用户计算机上的数据进行加密,直到支付赎金才可能解封的恶意软件。
- 常见的恶意软件:
- Phishing:网络钓鱼,指发送看似合法的电子邮件以诱骗收件人将其个人详细信息提供给电子邮件发件人的行为。
- Pharming:网域嫁接,指通过恶意代码将用户重定向到虚假网站,以便在用户不知情的情况下非法获取用户个人数据的行为。
- 注意:Pharming网域嫁接与phishing网络钓鱼的不同点在于,网域嫁接不需要用户采取任何操作就会转到虚假网站,而网络钓鱼需要用户点击虚假链接。
- DNS cache poisoning:DNS 缓存投毒,指更改了DNS域名服务器上的IP地址对应,以便用户在通过浏览器浏览时定向到虚假网站。
- Social engineering:社交工程,指通过人类互动欺骗用户,操纵用户来破坏正常的安全程序(如泄露密码、告知验证码等),以获得对计算机系统的非法访问或在他们的计算机上放置恶意软件的行为。
5.3.2 Explain how a range of solutions are used to help keep data safe from security threats 解释如何使用一系列解决方案来帮助保护数据免受安全威胁
• Including: 包括:
- access levels访问级别
- anti-malware including anti-virus and anti-spyware反恶意软件,包括反病毒和反间谍软件
- authentication (username and password, biometrics, two-step verification) 身份验证(用户名和密码、生物识别、两步验证)
- automating software updates自动软件更新
- checking the spelling and tone of communications检查通信的拼写和语气
- checking the URL attached to a link检查附加到链接
- firewalls防火墙
- privacy settings隐私设置
- proxy-servers代理服务器
- secure socket layer (SSL) security protocol安全套接字层 (SSL) 安全协议
- 常见的保护数据安全的方法包括:
- Access levels:访问级别。为不同的用户设置对计算机的访问限制,比如通过设置密码、user groups用户组等方式来使得不同的用户获得不同的访问权限。
- 注意:访问级别的设定与用户设置的level of security安全等级有关。安全等级越高,能访问的用户会越少。
- Anti-malware:反恶意软件,包括anti-virus反病毒软件和anti-spyware反间谍软件。这些反恶意软件通过扫描安装在系统中的软件和文件,根据已知的病毒和间谍软件数据库(typical spyware rules典型间谍软件规则或known file structures已知的文件结构等)来判断可能存在的恶意软件。
- Authentication:验证。通过使用一些证据(验证问题、手机号等)来证明用户身份。
- 常见的验证方式:
- Passwords and user names:密码和用户名。
- 注意:使用高强度密码,及时更换密码,错误输入几次后及时锁定账户,修改密码时需要有额外的提醒方式(发邮件、发短信等)。
- Biometrics:生物识别。通过识别独一无二的人类特征来作为身份验证。
- 常见例子:Fingerprint scans指纹扫描、Retina scans虹膜扫描、Face recognition面部识别、Voice recognition声音识别等。
- Two-step verification:两步验证法。需要通过两步来验证用户身份的方法。比如输入用户名和密码后还需要输入手机短信验证码。
- Passwords and user names:密码和用户名。
- 常见的验证方式:
- Automatic software updates:自动软件更新。软件的及时更新非常重要,因为更新中可能包含更新软件安全性或提高软件性能的补丁。
- 注意:有时候,不合适的更新也可能会破坏设备的系统稳定性。如果不小心更新了错误版本,需要重装系统、回滚到安装前的备份位置或卸载该更新。
- checking the spelling and tone of communications and URL links:检查通信和链接的拼写和语气。
- 需要特别检查的位置:
- The email address:邮件地址。有些看似是企业发送的邮件,实际上是从私人邮箱发出的。
- The tone of the email and bad spelling of words:邮件的语气及拼写错误。正规企业的邮件基本没有拼写错误,语气也非常正规。
- Misspelling of domain names in a link (typo squatting):链接中的域名拼写错误。伪装的链接一般会使用和正规企业域名非常相似的拼写来迷惑用户(比如Googlle、amazom等)。这种迷惑用户的情况被称为“typo squatting”。
- Suspicious links:可疑链接。邮件中一些链接看上去是陌生网站的网址,不要随意点击。
- Other errors:其他错误。比如付款链接未使用https等。
- 需要特别检查的位置:
- Firewalls:防火墙,指位于计算机和外部网络之间的软件或硬件。防火墙用于监视和过滤所有进入和传出的数据信息流量。如下图所示:
- Access levels:访问级别。为不同的用户设置对计算机的访问限制,比如通过设置密码、user groups用户组等方式来使得不同的用户获得不同的访问权限。
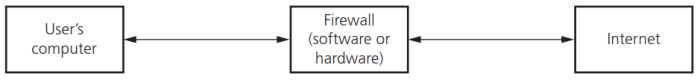
- 防火墙的作用:
- Examine the ‘traffic’ between user’s computer and a public network. 检查用户计算机和公共网络之间的流量
- Check whether incoming or outgoing data meets a given set of criteria. 检查进入或传出数据是否满足给定的标准
- Block the ‘traffic’ and give the user a warning if the data fails the criteria. 如果数据不符合标准,则阻止流量并向用户发出警告
- Log all incoming and outgoing ‘traffic’ to allow later interrogation by the user. 记录所有进入和传出的流量,以便用户以后进行查询
- Keep a list of all undesirable IP addresses and prevent access to them. 保留所有不需要的IP地址的列表并防止访问它们
- Help prevent viruses or hackers entering the user’s computer. 帮助防止病毒或黑客进入用户的计算机
- Warn users that some software on their system is trying to access an external data source. 警告用户其系统上的某些软件正在尝试访问外部数据源
- 防火墙可能失效的原因:
- it cannot prevent individuals, on internal networks, using their own hardware devices (e.g. modems, smartphones) to bypass the firewall. 不能阻止内部网络上的个人使用硬件设备(如调制解调器、智能手机等)绕过防火墙
- employee misconduct or carelessness cannot be controlled by firewalls (for example, control of passwords or user accounts). 员工的不当行为或粗心大意无法通过防火墙进行控制(如对密码或用户账户的控制)
- users on stand-alone computers can choose to disable the firewall, leaving their computer open to harmful ‘traffic’ from the internet. 独立计算机上的用户可以选择禁用防火墙,使得计算机对来自互联网的有害流量开放
- 防火墙的作用:
- Proxy servers:代理服务器,指作为处理互联网请求的中间服务器。如下图所示:
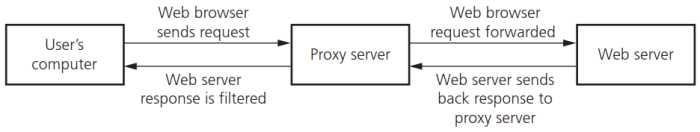
- 代理服务器的用途:
- Allow internet traffic to be filtered; block access to a website if necessary. 过滤互联网流量,必要时阻止访问网站
- Keep users’ IP addresses secret. 对用户的IP地址保密
- Block requests from certain IP addresses. 阻止来自特定IP地址的请求
- Prevent direct access to a web server. 防止直接访问网络服务器
- If an attack is launched, it hits the proxy server instead. 如果被攻击,收到攻击的会是代理服务器
- Direct invalid traffic away from web servers. 引导无效流量远离网络服务器
- Speed up access to information/data from a website. 加快从网站访问信息/数据
- Act as firewalls. 充当防火墙
- 代理服务器的用途:
- Privacy settings:隐私设置。通过社交网络或其他网站上的隐私设置来限制一些用户对个人资料或内容的访问。
- 隐私设置的用途:
- Stop websites collecting and using browsing data ('do not track'). 停止网站收集和使用浏览数据(防止网站追踪)
- A check to see if payment methods have been saved on websites. 检查付款方式是否已保存在网站上
- Safer browsing. 更安全的浏览
- Web browser privacy options (history, cookies). 浏览器隐私选项(历史记录、cookie)
- Website advertising opt-outs. 阻止弹出网站广告
- Not share location data. 不共享位置数据
- 隐私设置的用途:
- Secure sockets layer(SSL):安全链路层,指通过网络发送数据时使用的安全协议。
- SSL certificate:SSL证书,指一种用于验证网站的数字证书形式。如果提供的 SSL证书可验证,则可以认为浏览器和网站之间的通信或数据交换是安全的。
- 使用SSL进行数据传输的过程:
- 用户使用的浏览器发送消息,以便可以连接到受SSL保护的网站。
- 浏览器会要求web server网站服务器进行自我身份验证。
- 网站服务器接到要求,将自己的SSL证书发送给用户的浏览器。
- 浏览器对证书进行验证,如果没问题,则向网站服务器发送消息,允许进行数据传输。
- 网站服务器接到反馈,与浏览器建立安全的two-way data transfer双向数据传输,进行数据传输。