Edexcel IAL U1 revision - Section 3 (2018)
跳到导航
跳到搜索
【点此返回复习要点目录】


如遇到公式加载异常,请刷新页面!
Section 3 Supply 供给
- 大纲要求
1. The supply curve 供给曲线
a) The concept of "supply". 供给的概念
- Supply供给:生产者producers有意愿willing并且有能力able生产,其供给构成effective supply有效供给。经济学研究的供给理论基于effective supply。
- 普通的supply curve(横轴是quantity,纵轴是price,题目中没要求数字的时候可以画成没有数据的示意图。)

b) The distinction between movements along a supply curve and shifts of a supply curve. 沿供给曲线的点移动与整条供给曲线的线移动之间的区别
- Movement点移动
- Supply curve发生movement点移动的唯一原因是本商品的price发生了变化。Price上升会导致supply上升,反之亦然。
- Movement点移动时,量的增加称为extension,量的下降称为contraction。

- Shift线移动
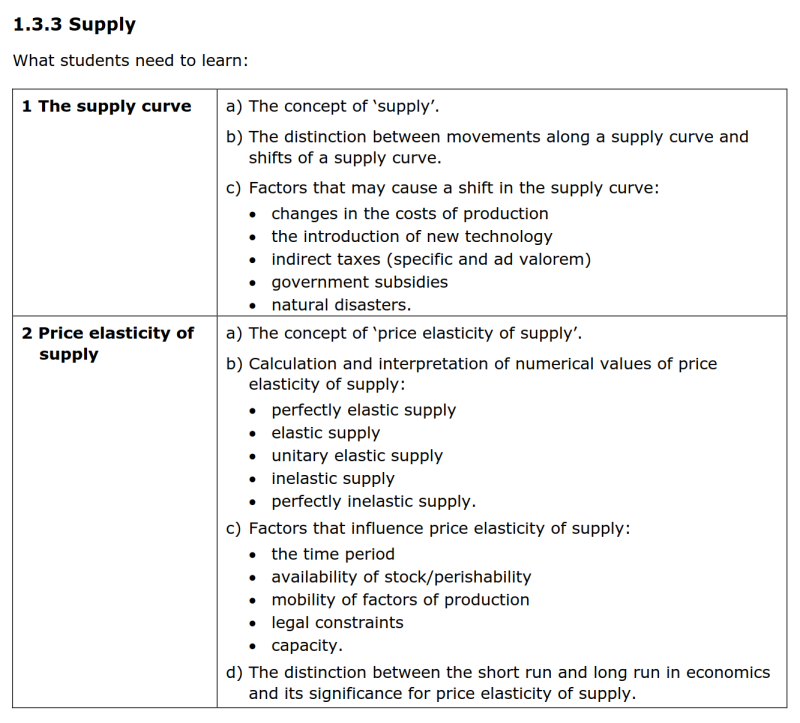
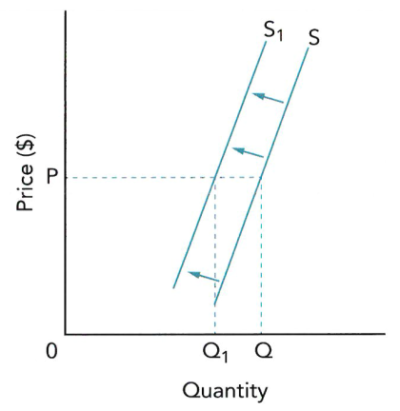
- 除了price因素之外,其他一切影响因素(即Non-price factors非价格因素)都会导致S曲线发生shift型移动。【参考1.3.3-1(c)】
- S曲线左移shift leftwards表示供给下降(左图所示),右移shift rightwards表示供给上升(右图所示)。


c) Factors that may cause a shift in the supply curve: 导致供给曲线发生线移的因素
• changes in the costs of production 生产成本的变化
• the introduction of new technology 新技术的引入
• indirect taxes (specific and ad valorem) 间接税(从量税与从价税)
• government subsidies 政府补贴
• natural disasters. 自然灾害
- changes in the costs of production 生产成本的变化
- 成本包括原材料成本(price of raw materials),能源成本(price of oil等),人力成本(wage等),维护成本(maintenance costs),分销成本(distribution costs)。成本越高,供给越少。
- the introduction of new technology 新技术的引入
- 技术水平越高,供给越多。
- indirect taxes (specific and ad valorem) 间接税(从量税与从价税)
- Taxation税收越多,供给越少。
- government subsidies 政府补贴
- Subsidy补贴越高,供给越多。
- natural disasters 自然灾害
- (一般和农业相关)天气或气候越好,供给越多。反之,天气或气候越差,供给越少。
- 除上述因素外,Supply还受以下因素影响:
- Size and nature of industry 行业的规模和性质
- 行业规模越大,供给越多。同时也会吸引更多生产者加入,不断扩大规模。
- 部分行业可能会限制供给(如稀有矿藏等)。
- Productivity 生产率
- 生产率越高,供给越多。
- Government policy 政府政策
- 政府政策越松(relaxation of certain types of legislation),供给越多。
- Prices of other products 其他商品价格。
- 竞争者涨价,意味着自家企业可以增加供给以填补市场需求空缺。反之,竞争者降价,意味着自家企业可能会因为市场份额被挤占而被迫减少供给。
- Size and nature of industry 行业的规模和性质
- 注意:使得Supply curve发生movement的原因为:
- Price (本商品的)价格
- 价格越高,供给越多。
- Price (本商品的)价格
2. Price elasticity of supply 价格供给弹性
a) The concept of ‘price elasticity of supply’. 价格供给弹性的概念
- PES:当价格发生一定程度的变化时,供给量对价格变化的反应程度responsiveness。
b) Calculation and interpretation of numerical values of price elasticity of supply: 价格供给弹性的计算及对其数值的解读
• perfectly elastic supply 完全弹性
• elastic supply (相对)有弹性
• unitary elastic supply 单位弹性
• inelastic supply (相对)缺乏弹性
• perfectly inelastic supply. 完全无弹性
- \(PES=\frac{percentage\space change\space in\space quantity\space supplied}{percentage\space change\space in\space price}=\frac{\displaystyle{\%}\Delta Q}{\displaystyle{\%}\Delta P}\), 其中\(\displaystyle{\%}\Delta Q=\frac{Q_{2}-Q_{1}}{Q_{1}}\), \(\displaystyle{\%}\Delta P=\frac{P_{2}-P_{1}}{P_{1}}\)
- PES通常为正数,因为价格变化和供给量变化一般为正相关。
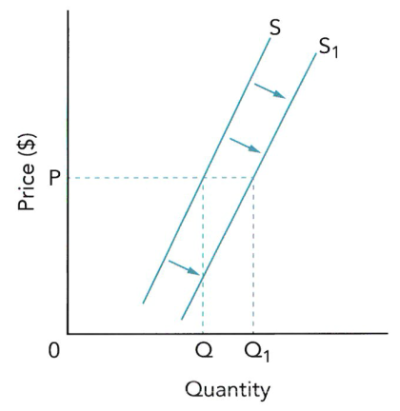
- PES也分为perfectly elastic, (highly) elastic, unitary elasticity, (highly) inelastic, perfectly inelastic。PES弹性数值分类与PED一致,图像如下表所示。(图像为整条Supply curve中的很小一段的截图)
| Elasticity description | Value | PES Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| perfectly elastic 完全弹性 |
∞ infinity |
|
| elastic 富有弹性 |
>1 | 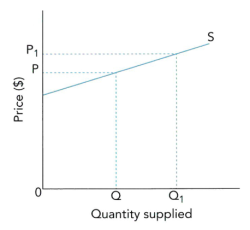
|
| unitary elastic (始终保持1的)单位弹性 |
1 | 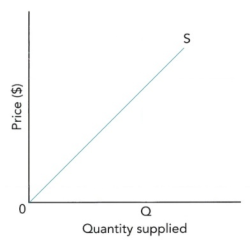
|
| inelastic 缺乏弹性 |
0~1 | 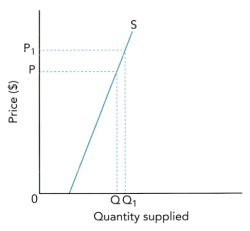
|
| perfectly inelastic 完全无弹性 |
0 | 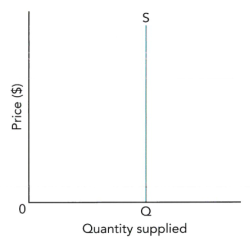
|
c) Factors that influence price elasticity of supply: 影响供给价格弹性的因素
• the time period 时间
• availability of stock/perishability 库存的可获得性与易腐性
• mobility of factors of production 生产要素的可移动性
• legal constraints 法律限制(门槛)
• capacity. 产能(空余产能,即距离生产上限的距离)
- the time period 时间
- 时间越长,PES越大。(生产要素可能无法在短期内进行转换;技术会进步)
- availability of stock/perishability 库存的可获得性与易腐性
- 商品存货越多,PES越大。
- 商品越方便长时间保存,PES越大。
- mobility of factors of production 生产要素的可移动性
- 生产替代品主要指同一生产线可生产的多种产品。该商品生产线可生产的商品种类越多,生产要素的可移动性越大,该商品的PES越大。
- legal constraints 法律限制(门槛)
- 进入该行业门槛越低,PES越大。
- capacity 产能(空余产能,即距离生产上限的距离)
- 空余产能越多,PES越大。
d) The distinction between the short run and long run in economics and its significance for price elasticity of supply. 经济中短期与长期的区别;其对供给价格弹性的重要性
- short run:短期。至少有一个at least one生产要素保持不变unchanged。
- long run:长期。所有生产要素都可以变化variable。但技术、法律条文、社会文化等key inputs关键性投入保持不变。
- very long run:超长期。所有生产要素都可以变化,而且技术、法律条文、社会文化等key inputs关键性投入也可以发生变化。
- 三者的终极判断标准:生产要素的变化性(注意:和时间长短无关,不同行业的长短期并不相同)
- 企业通过查看PES的情况,可以respond to changing market conditions应对变化的市场情况,确定商品的供给能否对价格变动做出迅速调整,并根据情况制定相应的生产计划和对策。
- 如商品市场可以考虑建仓库等。
- 农业市场一般PES偏小inelastic,要注意需求的波动对价格的大幅影响,注意防范风险。