Edexcel IAL U3 revision - Section 5 (2018)
如遇到公式加载异常,请刷新页面!
Section 5 Government intervention 政府干预
- 大纲要求
1. Government intervention in product markets产品市场中的政府干预
a) The case for government intervention. 政府干预的例子
- 【参考3.3.5-1(b)、3.3.5-1(c)、3.3.5-1(d)】。
b) Measures to control monopolies and mergers: 控制垄断与兼并的手段:
• price regulation 价格监管
• profit regulation 利润监管
• quality standards 质量标准
• performance targets 绩效目标
• referral to regulatory authorities 转交监管机构
• legislation to control mergers and takeovers. 立法控制兼并与收购
- price regulation 价格监管
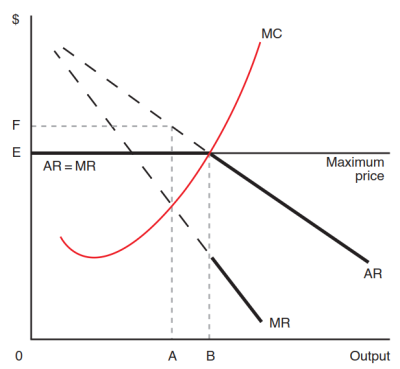
- 通过maximum price等手段,控制垄断产品的市场价格,使其无法收取高价格以谋取太多超额利润。(如下图所示)
- 政策的问题:
- 政府很难准确确定价格的位置,容易出现government failure政府失灵。
- 企业赚取的supernormal profits超额利润下降,影响企业投资开发,dynamic efficiency动态效率下降。
- 政策的问题:
- 通过maximum price等手段,控制垄断产品的市场价格,使其无法收取高价格以谋取太多超额利润。(如下图所示)
- profit regulation 利润监管
- 规定企业只能赚取一定水平的利润(通常是成本的一定百分比)。
- 政策的问题:
- 政府和企业之间存在asymmetric information不对称信息,政府很难准确确定应赚的利润水平。
- 企业无需致力于降低成本,效率下降,存在资源浪费。
- 由于很多时候是按照资本投入计算百分比,因此鼓励企业多使用capital生产要素而减少诸如labour的其他生产要素使用。
- 政策的问题:
- 规定企业只能赚取一定水平的利润(通常是成本的一定百分比)。
- quality standards 质量标准
- 政府要求企业提供符合一定质量标准的产品。
- 政策的问题:
- 企业可能并不按照标准生产、想办法规避标准或迫使政府修改标准。
- 政策的问题:
- 政府要求企业提供符合一定质量标准的产品。
- performance targets 绩效目标
- 政府为企业设定一系列生产绩效目标,要求企业达成。
- 政策的问题:
- 企业可能并不按照目标生产、想办法规避目标或迫使政府修改目标。
- 政府设定的目标可能会频繁修改。
- 政策的问题:
- 政府为企业设定一系列生产绩效目标,要求企业达成。
- referral to regulatory authorities 转交监管机构
- 政府对涉嫌垄断的企业进行调查,一旦证实则做出相应处罚。
- legislation to control mergers and takeovers. 立法控制兼并与收购
- 政府对可能形成垄断的兼并收购交易进行审查,阻止一些企图垄断市场的合并。
c) Measures to promote competition and contestability: 促进竞争和可竞争性的措施:
• tax incentives and grants to promote small businesses and FDI 使用税收优惠和补贴促进小企业发展和外国直接投资
• deregulation 放松管制(去规则化)
• privatisation 私有化
• competitive tendering for public sector contracts 公共部门的合同竞标
• trade liberalisation. 贸易自由化
- tax incentives and grants to promote small businesses and FDI 使用税收优惠和补贴促进小企业发展和外国直接投资
- 通过税收减免、补贴和从国外招商引资等方式鼓励大量企业进入该行业,以增加企业数量,促进竞争。
- deregulation 放松管制(去规则化)
- 允许私企进入原本只有国企才能进入的行业。
- 简化进入行业手续。
- 通过税收优惠、补贴等手段鼓励企业进入该行业。
- 政策的问题:
- 企业着眼于赚取利润,因此只会专注于能赚钱的领域,无法带来良好收益的领域便减少或不再生产。
- 政策的问题:
- privatisation 私有化
- 鼓励国企转变为私企,提高生产效率,降低成本,增加种类创新。
- competitive tendering for public sector contracts 公共部门的合同竞标
- 通过公开竞标的方式进行方案的遴选,促进竞争,降低成本。
- trade liberalisation. 贸易自由化
- 移出各类贸易壁垒,鼓励自由贸易,促使本国企业提升效率。
d) Measures to protect suppliers and employees: 保护供应商和员工的措施:
• local sourcing of raw materials and components 在当地采购原材料和组件
• employment legislation to protect workers from exploitation 立法保护工人免受剥削
• barriers to entry of foreign firms 针对外国企业的进入壁垒
• restrictions on the monopsony power of firms 对企业垄断力的限制
• nationalisation. 国有化
- local sourcing of raw materials and components 在当地采购原材料和组件
- 政府要求外来企业(尤其是跨国企业)在当地采购原材料和雇佣劳动力,既可以留下一部分企业利润,又可以带动当地企业发展,促进当地就业。
- employment legislation to protect workers from exploitation 立法保护工人免受剥削
- 政府通过立法保护工人的权利,减少剥削。
- 政府可建立或鼓励独立的机构(比如工会)帮助维护工人的利益。
- 政府可以要求企业自主做好工人权益的保障。
- barriers to entry of foreign firms 针对外国企业的进入壁垒
- 要求外国企业必须满足一系列要求才能进入本国发展,比如留下一部分利润、保护环境、雇佣当地劳动力、分享技术等。
- restrictions on the monopsony power of firms 对企业垄断力的限制
- 政府通过立法限制垄断产生(比如反垄断法)。
- 政府可建立独立的机构审查企业垄断问题。
- 政府可以要求企业自主监督。
- nationalisation. 国有化
- 国有化能够使得企业更加关注人们的福利。
e) The impact of each measure on: 每项措施对以下方面的影响:
• price 价格
• profit 利润
• efficiency 效率
• quality 质量
• choice. 选择
- 【参考3.3.5-1(b)、3.3.5-1(c)、3.3.5-1(d)】。
f) Limits to government intervention: 政府干预的限制:
• regulatory capture 监管捕获
• asymmetric information/information gaps 不对称信息/信息缺口
• inadequate resources 资源不足
• lack of regulatory power. 缺乏监管力度
- regulatory capture 监管捕获
- 原本应该约束企业行为的部门现在却替企业说话,称为监管捕获。这可能是因为收了贿赂,或者被企业威胁。
- asymmetric information/information gaps 不对称信息/信息缺口
- 政府对企业的了解远不如企业本身,因此为企业确定的目标不一定准确。
- inadequate resources 资源不足
- 政府用于调控的资源不足,比如没有足够的钱发放补贴。
- lack of regulatory power. 缺乏监管力度
- 政府如果力量较弱,很难约束大型企业。
2. Government intervention in labour markets 劳动力市场中的政府干预
a) The case for government intervention. 政府干预的案例
- 【参考3.3.5-2(b)】。
b) Types of government intervention in labour markets and their effects: 劳动力市场中政府干预的类型及其效果:
• maximum wage controls 最高工资控制
• minimum wage controls 最低工资控制
• direct taxes e.g. national insurance contributions; corporation tax 直接税,例如国民保险缴款;公司税
• measures to reduce geographical and occupational immobility of labour 减少劳动力地域间不流动性和职业间不流动性的措施
• measures to reduce discrimination and exploitation. 减少歧视和剥削的措施
- maximum wage controls 最高工资控制
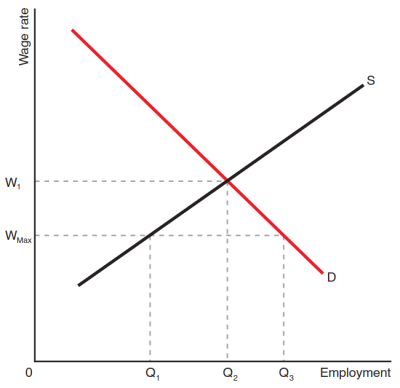
- 政府通过立法等手段限制高管等高薪人员的工资水平,缩小贫富差距。(如图所示)
- 政策的问题:
- 愿意提供劳动力的人下降,很多高端人才可能寻求海外发展。
- 影响人们的工作热情,效率下降。
- 该手段的效果与WED和WES的大小有关。
- 政策的问题:
- 政府通过立法等手段限制高管等高薪人员的工资水平,缩小贫富差距。(如图所示)
- minimum wage controls 最低工资控制
- 政府通过立法等手段提高低收入人群的工资水平,缩小贫富差距。
- 政策的问题:
- 该手段的效果与WED和WES的大小有关。
- 企业对劳动力的需求下降,而劳动力供给增加,可能出现失业。
- 政策的问题:
- 政府通过立法等手段提高低收入人群的工资水平,缩小贫富差距。
- direct taxes e.g. national insurance contributions; corporation tax 直接税,例如国民保险缴款;公司税
- 政府通过改变企业和工人的税赋情况,来调节劳动力的供求情况。
- 政策的问题:
- 如果税收太高,会降低工人的劳动热情。
- 企业税收太高,会影响其投资。
- 企业为工人缴纳的税收太高,会促使企业采用capital来取代labour。
- 政策的问题:
- 政府通过改变企业和工人的税赋情况,来调节劳动力的供求情况。
- measures to reduce geographical and occupational immobility of labour 减少劳动力地域间不流动性和职业间不流动性的措施
- Improve education and training. 改进教育和培训。
- Provide specific training for workers to target skills shortages in the economy. 为工人提供专门培训,以解决经济中的技能短缺问题。
- Provide subsidies to workers who have to move house to get a job. 为必须搬家找工作的工人提供补贴。
- Provide help with housing for workers who get jobs outside their local area. 为在当地以外找到工作的工人提供住房帮助。
- Increase knowledge of job opportunities. 增加对工作机会的了解。
- Subsidise employers who take on unemployed individuals from groups in the labour market. 补贴从劳动力市场中招聘失业人员的雇主。
- Help workers with job applications. 帮助工人申请工作。
- Reform the tax and benefits system or increasing the minimum wage. 改革税收和福利制度或提高最低工资。
- Reduce discrimination in the labour market. 减少劳动力市场的歧视。
- measures to reduce discrimination and exploitation. 减少歧视和剥削的措施
- 劳动力市场中常见的歧视:age年龄歧视、gender性别歧视、race种族歧视。
- 可采用的措施:
- Pass laws that make it illegal to discriminate on employees. 通过法律将歧视员工定为非法。
- The law and minimum wages also help to stop the exploitation of workers. 法律和最低工资也有助于制止对工人的剥削。
- International cooperation is needed to help stop exploitation. 需要国际合作来帮助制止剥削。
